Market Insight:
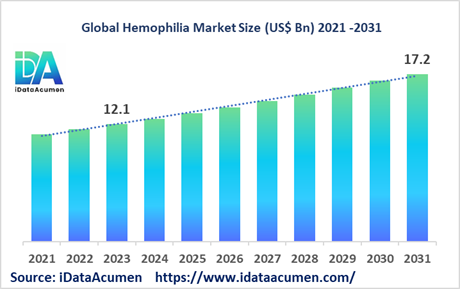
The Hemophilia Market size is expected to reach US$ 17.2 billion by 2031, from US$ 12.1 billion in 2023, at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period. Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder where blood fails to clot properly due to lack of clotting factors VIII (Hemophilia A) or IX (Hemophilia B). It is treated by replacing the missing clotting factors to prevent or stop bleeding episodes. Key drivers include development of extended half-life factors requiring less frequent dosing and emergence of prophylaxis as the standard of care.
The Hemophilia Market is segmented by product, treatment type, therapy, age group, and region. By product, the market is segmented into Hemophilia A, Hemophilia B, inhibitors, Von Willebrand Disease, and others. Hemophilia A is the largest segment due to higher incidence and ongoing research into novel treatments like gene therapy. For instance, BioMarin’s valrox gene therapy for Hemophilia A is under review by the FDA.
Epidemiology Insights:
- Hemophilia A affects 1 in 5,000 male births worldwide, while Hemophilia B affects 1 in 25,000 male births. Overall prevalence is around 400,000 globally.
- In the US, Hemophilia A prevalence is estimated around 20,000, while Hemophilia B prevalence is approx 4,000. In the EU, the estimated prevalence of Hemophilia A is around 37,000.
- Due to the X-linked recessive nature of hemophilia, it occurs almost exclusively in males. However, carrier testing and prenatal diagnosis becoming more common.
- Developed countries like the US, UK, France, Germany have a higher diagnosed prevalence compared to developing countries where diagnosis is poorer. This represents a growth opportunity.
- Hemophilia is designated as a rare disease in the US and Europe.
Market Landscape:
- There are still unmet needs like reduction in treatment burden, management of inhibitors, and affordable access to treatment in developing markets.
- Current standard of care is replacement of clotting factors, either on-demand or as prophylaxis. Some approved therapies are Advate, Kogenate FS, Novoeight, Eloctate.
- Several novel non-factor therapies like gene therapy, RNAi, and bispecific antibodies are in late stage clinical trials to enable lifetime correction of hemophilia.
- Gene therapy is a breakthrough approach with potential to transform care. Lead assets like BioMarin’s valrox and Pfizer/Sangamo’s giroctocogene fitusiran have shown long term factor activity with a single infusion.
- The market has a mix of pharma giants like Takeda, Sanofi, and Pfizer as well as biotechs focused on novel approaches like gene therapy.
Market Scope:
|
Key Insights |
Description |
|
The market size in 2023 |
US$ 12.1 Bn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
4.5% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 17.2 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2031 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Takeda, CSL Behring, Pfizer, BioMarin, Roche, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Bayer, Grifols, Octapharma, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum, Biogen, Freeline Therapeutics, Sangamo Therapeutics, Spark Therapeutics, uniQure, Catalyst Biosciences, Dimension Therapeutics, Eloxx Pharmaceuticals, ObsEva |
Market Drivers:
Emergence of Novel Therapies
The emergence of novel non-factor replacement therapies such as gene therapy, RNA interference (RNAi), and bispecific antibodies presents significant growth opportunities in the Hemophilia market. These innovative platforms have the potential to transform the standard of care by enabling durable correction of the underlying genetic defect. Gene therapy involves delivering functional copies of the defective clotting factor gene to express the missing protein. Both AAV-based gene transfers and lentiviral approaches are being explored. Companies like BioMarin, Sangamo Therapeutics and Pfizer have leading clinical programs. RNAi therapies use small interfering RNA to reduce production of antithrombin, thus rebalancing coagulation. Examples are fitusiran by Sanofi/Alnylam and inclisiran by The Medicines Company. These therapies can lower bleeds and factor usage. If approved, they may significantly expand the patient pool and market size.
Prophylaxis as Standard of Care
The growing adoption of prophylactic factor replacement therapy over on-demand treatment is a key driver. Clinical evidence has demonstrated that prophylactic infusion of clotting factors 1-3 times a week significantly reduces bleeding episodes and long-term joint damage compared to on-demand therapy. International and national guidelines now recommend primary prophylaxis as the optimal therapy for people with severe hemophilia. Increasing awareness among patients and clinicians regarding the benefits of prophylaxis is leading to a rise in adoption rates. The expanding prophylactic treatment population will result in consistent clotting factor consumption and require novel technologies like extended half-life factors to reduce infusion burden. Prophylaxis penetration is still low in emerging markets, indicating significant room for growth.
Extension in Half-life of Clotting Factors
The development of extended half-life (EHL) factor concentrates that require less frequent dosing is driving market growth. Conventional factors have half-lives of 8-12 hours, requiring 2-3 infusions per week. EHL factors use technologies like PEGylation, fusion with Fc fragment and albumin binding to improve the half-life to up to 1.5 times that of conventional factors. Products like Eloctate, Afstyla, Jivi, and Esperoct have shown clinical efficacy and safety in reducing infusion burden. Adoption of EHL factors will likely be significant in patients on prophylaxis. Companies are developing next generation and follow-on biologics. Regulatory approval of new EHL factors such as Roche’s Hemlibra, with weekly or longer dosing, can fuel market growth by improving compliance and quality of life.
Improving Diagnosis and Access to Care
Better diagnosis and increasing access to treatment in emerging economies provides growth opportunities. Hemophilia is still underdiagnosed in developing regions. Advancements in diagnostic technology like point-of-care testing and genome sequencing are facilitating faster diagnosis. Neonatal screening programs help early diagnosis and initiation of therapy. Government and payer initiatives to increase patient education and treatment availability, establish hemophilia treatment centers (HTCs), and add the disorder to national healthcare programs will drive patient pool growth. Pharmaceutical companies are expanding operations in high potential markets to tap the underpenetrated patient pool. As diagnosis and access to modern treatments improve, a larger proportion of patients will be treated, benefiting the market outlook.
Market Opportunities:
Gene and Cell Therapy in Hemophilia
Gene therapy and gene-modified cell therapy are emerging opportunities which can revolutionize hemophilia care in the long run. Gene therapy involves delivering functional copies of the defective coagulation factor gene into patient’s cells, potentially correcting the disorder. A one-time infusion can lead to stable factor VIII or IX expression within the therapeutic range for years, reducing or eliminating the need for exogenous factors. Gene therapy candidates by BioMarin, Spark Therapeutics and Sangamo Therapeutics have shown sustained factor activity levels in clinical studies. Cell therapy using gene-edited stem cells or T cells are also being explored. These platforms can help overcome challenges associated with viral gene delivery. If approved, gene and cell therapies may significantly expand the patient pool and disrupt the market.
Developing Novel Non-factor Replacement Therapies
Companies are investing significantly in R&D of novel non-factor replacement therapies which do not rely on exogenous coagulation factors. Besides gene therapy, key approaches include RNA interference, bispecific antibodies, and complement inhibitors. RNAi therapies utilize small interfering RNA to inhibit natural anticoagulants, rebalancing the coagulation cascade. Alnylam’s fitusiran and Dicerna’s nedosiran have demonstrated promising safety and efficacy in reducing bleed rates. Roche’s Hemlibra, an anti-factor IXa/X bispecific antibody has shown clinical benefit in patients with inhibitors. It is the first approved non-factor therapy. These innovative therapies with favorable dosing can help overcome challenges with current options and unlock new revenue prospects.
Exploring Novel Administration Methods
Novel administration methods like oral, subcutaneous and transdermal factor delivery are being explored to minimize infusion burden and improve patient compliance to replacement therapy. Subcutaneous administration is less invasive and enables self-dosing at home. Rebinyn, Sevenfact and Jivi are approved subcutaneous factors. Oral administration is convenient but poses challenges for peptide/protein stability and absorption. Transdermal delivery using microneedle patches or chemical modification to enhance skin penetration is also being evaluated. Companies like Catalyst Biosciences, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, and Xenetic Biosciences have early pipeline candidates utilizing alternative delivery methods. If technologically feasible and clinically effective, these can improve ease of administration for patients.
Emerging Markets Untapped Potential
Emerging markets represent significant growth opportunities owing to the high unmet need and underpenetration of diagnosis and therapy. According to estimates, around 75% of hemophilia cases globally remain undiagnosed, with the majority in developing countries. Lack of awareness, financial constraints, and limited access to treatment centers hamper growth. Pharmaceutical companies are expanding operations in high potential markets and partnering with local governments to improve patient outreach and access through diagnosis programs, financing support and infrastructure development. With improving healthcare expenditure and insurance coverage, these untapped markets are expected to drive the next wave of growth and represent immense commercial potential.
Market Trends:
Adoption of Standard Treatment Guidelines
Increasing issuance and adoption of standardized treatment recommendations and guidelines for hemophilia management by health authorities and medical societies is a key trend benefitting the market. Evidence-based guidelines help streamline care across different demographics and clinical settings. The World Federation of Hemophilia’s guidelines provide a common standard for the global community. Other national bodies like the American Society of Hematology (ASH), UK Haemophilia Centre Doctors' Organization (UKHCDO), Indian Haemophilia Society and European Association for Haemophilia and Allied Disorders (EAHAD) also regularly update guidelines. They endorse prophylaxis therapy,recommend comprehensive care at hemophilia treatment centers and provide guidance on optimal treatment approaches for issues like inhibitors. Adoption of such standards improves clinical outcomes.
Public-Private Partnerships Expanding Access
Public-private partnerships between governments, non-profits and industry players to improve awareness and increase access to care in underserved regions is a growing trend. Organizations like World Federation of Hemophilia and groups like Save One Life partner with local health authorities and companies to conduct screening, establish treatment centers, provide education and make modern therapies available through subsidized access programs. For instance, Pfizer collaborates with WFH on developing programs tailored for India, Brazil, Colombia and African countries. Such partnerships leverage strengths of stakeholders to address challenges around affordability and availability of treatment faced in these markets. They play a pivotal role in creating healthcare infrastructure and ensuring comprehensive care.
Shift Towards Patient-Centric Digital Solutions
Pharmaceutical players and health tech startups are increasingly integrating digital technology like wearables, apps and software platforms to improve patient engagement, monitoring and data aggregation. Tools like Fitbit health trackers customized with hemophilia-specific analytics, smartphone apps like myPKFiT and HemMobile, and patient portals like Shire’s Biohub provide patients access to historical infusions data, enable real-time monitoring of health parameters, and simplify reporting. Robust data analytics can provide insights to guide personalized care. Other patient-centric solutions like home infusion devices are also emerging. These digital health solutions empower patients with information, convenience and control over disease management.
Use of Real World Data and Evidence
The utilization of real world data (RWD) and real world evidence (RWE) is rising in hemophilia therapeutic research and development. RWD derived from sources like patient registries provides insights into clinical management and ‘real world’ product performance to support value and outcomes-based care. For example, national registries like FranceCoag Network informed clinical guidelines on prophylaxis therapy. RWE from such datasets is increasingly being used to complement clinical trial findings and guide regulatory decision making on efficacy, optimal use and safety of hemophilia therapies. Companies like Sanofi and Pfizer have collaborated with organizations like PatientShare&Registries to support therapeutics development and commercialization using RWD and RWE.
Market Restraints:
High Cost Burden of Hemophilia Therapies
The substantial cost burden associated with lifelong hemophilia care is a key market restraint. Factor replacement therapeutics and the comprehensive care required are costly, with the average per-patient expenditure estimated between $270,000 to $1 million annually in developed markets. Conventional factor products are already expensive and newer long-acting factors and non-factor agents are expected to be costlier. Lack of insurance coverage and limited reimbursement in several countries makes modern treatment unaffordable for the majority. High co-pays and deductibles still leave patients with out of pocket expenses in developed regions. While companies offer copay assistance programs, their sustainability is uncertain. The exorbitant costs of novel therapies like gene and cell therapy also raises affordability concerns, which can hinder adoption.
Inhibitor Formation Neutralizing Standard Therapy
Inhibitor formation is a serious complication where the patient’s immune system develops antibodies against the replacement factor, rendering standard therapy ineffective. Inhibitors develop in around 30% of hemophilia A and 3-5% of hemophilia B patients. Managing hemorrhage in those with inhibitors is complex and associated with higher morbidity. Costs can be 2-5 times higher. While bypassing agents can overcome low titer inhibitors, they are less effective on high titer inhibitors. Patients require immunosuppression which increases treatment expense and comorbidities. The population with inhibitors thus represents an unmet need. Overcoming this key challenge through new therapies and technologies remains a key focus area.
Underdiagnosis in Emerging Economies
Lack of awareness and diagnostic capabilities leading to significant underdiagnosis in emerging countries is a major limiting factor. According to estimates, around 75% of hemophilia cases globally remain undiagnosed. The majority of these patients reside in developing regions like the Middle East, Africa, Asia and Latin America. Factors like limited public knowledge, shortage of trained healthcare professionals, lack of specialized labs and equipment hamper diagnosis, especially in rural and remote areas. Delay in diagnosis leads to uncontrolled bleeding episodes, debilitating joint damage and premature mortality. While companies and governments are promoting screening, the infrastructure bottlenecks highlighting the need for capacity building to address this gap.
Recent Developments:
|
Product Launch |
Company Name |
|
In May 2023, Takeda launched Reybien, an extended half-life factor VIII treatment for hemophilia A. It is approved for adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older in the US. Reybien offers potentially less frequent dosing. |
Takeda |
|
In June 2021, CSL Behring launched Haegarda, the first C1 inhibitor for subcutaneous prophylaxis in pediatric hemophilia A patients with inhibitors. Haegarda provided 60% reduction in bleeds. |
CSL |
|
In November 2020, Sanofi launched Nexviadyme, an extended half-life factor VIII treatment. Nexviadyme showed prolonged protection from bleeds of up to 5 days in clinical trials. |
Sanofi |
|
Merger/Acquisition |
Involved Companies |
|
In April 2023, Pfizer acquired gene therapy biotech Vivet Therapeutics for $639 million upfront. The deal expands Pfizer's gene therapy capabilities in hemophilia and other rare diseases. |
Pfizer |
|
In 2019, Roche acquired Spark Therapeutics for $4.8 billion to access its gene therapy portfolio including Hemophilia A candidate SPK-8011. |
Roche |
|
In 2018, Takeda acquired Shire for $62 billion, gaining Shire’s leading hemophilia franchise including Advate and Adynovate. |
Takeda |
Market Regional Insights:
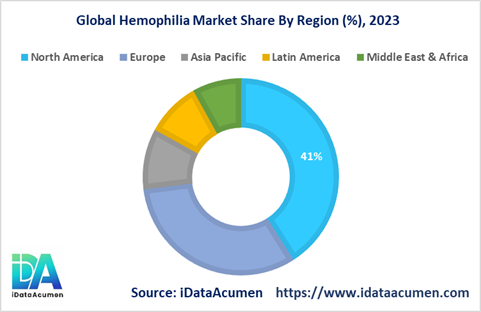
- North America is expected to be the largest market for Hemophilia during the forecast period, accounting for over 41% of the market share in 2023. The growth is driven by high diagnosis rates and access to advanced treatments.
- Europe market is expected to be the second-largest market for Hemophilia, accounting for over 32% of the market share in 2023. The established healthcare infrastructure and reimbursement policies support the market growth.
- The Asia Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Hemophilia, with a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period. The increasing investment in healthcare and growing patient pool are key regional growth drivers.
Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type
- Hemophilia A
- Hemophilia B
- Inhibitors
- Von Willebrand Disease
- Others
- By Treatment Type
- On-demand
- Prophylaxis
- Extended Half-life Factors
- Hemostats
- Others
- By Therapy
- Plasma-derived Factors
- Recombinant Factors
- Non-factor Replacement
- Others
- By Age Group
- Adults (>18 years)
- Pediatric (<18 years)
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- E-commerce
- Clinics
- Others
- By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- U.K.
- Spain
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- Israel
- South Africa
- North Africa
- Central Africa
- Rest of the Middle East
- North America
Top companies in the Hemophilia Market:
- Takeda
- CSL Behring
- Pfizer
- BioMarin
- Roche
- Novo Nordisk
- Sanofi
- Bayer
- Octapharma
- Grifols
- Swedish Orphan Biovitrum
- Biogen
- Freeline Therapeutics
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Spark Therapeutics
- uniQure
- Catalyst Biosciences
- Dimension Therapeutics
- Eloxx Pharmaceuticals
- ObsEva