Market Analysis:
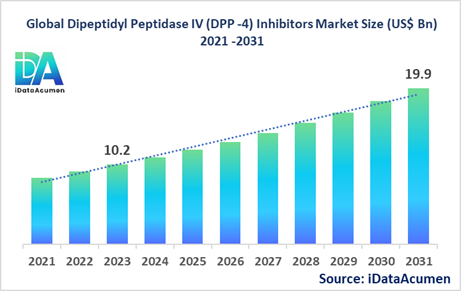
The Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market had an estimated market size worth US$ 10.2 billion in 2023, and it is predicted to reach a global market valuation of US$ 19.9 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 8.7% from 2024 to 2031.
DPP-4 inhibitors are a class of oral medications used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. They work by inhibiting the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), which breaks down incretin hormones like glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release and suppressing glucagon secretion when blood sugar levels are high. The primary advantage of DPP-4 inhibitors is their ability to improve glycemic control with a low risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and weight gain. The rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes globally, coupled with the increasing adoption of these medications as a part of combination therapy regimens, is driving the market growth.
The Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market is segmented by drug class, route of administration, distribution channel, disease indication, patient demographics, and end-user, among others. By drug class, the market is segmented into sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin, vildagliptin, and others. The sitagliptin segment is expected to hold a significant market share due to its widespread adoption and availability of generic versions, leading to cost-effectiveness.
Epidemiology Insights:
- The disease burden of type 2 diabetes is substantially high across major regions, with North America and Europe accounting for a significant proportion of cases. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing a rapid rise in the prevalence of diabetes due to lifestyle changes and urbanization.
- Key epidemiological trends include the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes among younger populations, rising obesity rates, and a shift towards sedentary lifestyles. These factors are driving the demand for effective therapeutic interventions, including DPP-4 inhibitors.
- According to the International Diabetes Federation, in 2021, an estimated 537 million adults aged 20-79 years were living with diabetes, with type 2 diabetes accounting for the majority of cases.
- The increasing patient population with type 2 diabetes presents significant growth opportunities for the DPP-4 inhibitors market, as these medications are widely prescribed for the management of this chronic condition.
- Type 2 diabetes is not considered a rare disease, as it is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases globally.
Market Landscape:
- Despite the availability of various treatment options, there remain unmet needs in the DPP-4 inhibitors market, particularly in terms of improving patient compliance, addressing side effects, and developing more effective combination therapies.
- Current treatment options for type 2 diabetes include metformin (first-line therapy), sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 agonists, insulin, and DPP-4 inhibitors. Approved DPP-4 inhibitors include sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin, and vildagliptin, among others.
- Upcoming therapies and technologies in the market include novel DPP-4 inhibitors with improved efficacy and safety profiles, as well as combination therapies that incorporate DPP-4 inhibitors with other antidiabetic agents.
- Breakthrough treatment options currently being developed include oral and injectable formulations of GLP-1 agonists, dual agonists targeting multiple receptors, and novel insulin delivery systems.
- The DPP-4 inhibitors market is dominated by branded drug manufacturers, with a few large pharmaceutical companies holding a significant market share. However, the presence of generic drug manufacturers is expected to increase as patents expire.
Market Report Scope:
|
Description |
|
|
The market size in 2023 |
US$ 10.2 Bn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
8.7% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 19.9 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Merck & Co., Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer Inc., Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer AG, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Novo Nordisk A/S, AbbVie Inc., Mylan N.V., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Cipla Inc., Lupin Limited, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. |
Market Drivers:
Rising Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes globally is a significant driver for the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market. According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults aged 20-79 were living with diabetes in 2021, and this number is projected to rise to 783 million by 2045. The growing burden of type 2 diabetes, fueled by factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and an aging population, has led to an increased demand for effective therapeutic interventions, including DPP-4 inhibitors.
Recent advancements in diabetes management guidelines and treatment algorithms have recognized the importance of DPP-4 inhibitors as a key component of combination therapy regimens. This has further driven the adoption of these medications among healthcare professionals and patients, contributing to the market's growth.
Favorable Safety and Tolerability Profile
DPP-4 inhibitors are generally well-tolerated and have a favorable safety profile compared to some other antidiabetic medications. They are associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels) and weight gain, which are common side effects of certain diabetes treatments. This advantage has made DPP-4 inhibitors an attractive option for patients who are sensitive to these adverse effects or have comorbidities that may be exacerbated by weight gain or hypoglycemia.
The safety and tolerability of DPP-4 inhibitors have been demonstrated through numerous clinical trials and real-world evidence, fostering confidence among healthcare professionals in prescribing these medications.
Development of Fixed-Dose Combination Therapies
Pharmaceutical companies have been actively developing fixed-dose combination therapies that incorporate DPP-4 inhibitors with other antidiabetic agents. These combination products offer improved glycemic control and convenience for patients by combining multiple mechanisms of action in a single pill.
The availability of fixed-dose combination therapies has simplified treatment regimens and enhanced patient adherence, driving the growth of the DPP-4 inhibitors market. Examples of such combinations include Qtern (dapagliflozin and saxagliptin) by AstraZeneca and Steglujan (ertugliflozin and sitagliptin) by Merck & Co.
Increasing Adoption in Emerging Markets
While developed markets like North America and Europe have traditionally dominated the DPP-4 inhibitors market, there is a growing adoption of these medications in emerging markets, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. Factors such as rising disposable incomes, improved access to healthcare, and increasing awareness about the management of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes have contributed to the market's growth in these regions.
Pharmaceutical companies have recognized the potential in emerging markets and are taking steps to expand their presence and make DPP-4 inhibitors more accessible to patients in these regions.
Market Opportunities:
Expansion into Emerging Therapeutic Areas
While DPP-4 inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, ongoing research is investigating their potential therapeutic applications in other areas. Promising opportunities exist in conditions such as obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and certain cardiovascular diseases.
For instance, studies have shown that DPP-4 inhibitors may have beneficial effects on weight management and metabolic parameters, making them potential candidates for the treatment of obesity. Additionally, their ability to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate hormone levels holds promise for the management of PCOS.
Expanding the therapeutic indications of DPP-4 inhibitors could open up new market avenues and drive further growth in the industry.
Novel Drug Delivery Systems
While most currently available DPP-4 inhibitors are administered orally, there is an opportunity to explore alternative drug delivery systems. Developments in novel drug delivery technologies, such as transdermal patches, nasal sprays, or injectable formulations, could enhance patient convenience and adherence.
Alternative drug delivery systems may offer improved bioavailability, sustained release profiles, or targeted delivery, potentially improving the efficacy and safety of DPP-4 inhibitors. These advancements could differentiate new products in the market and cater to specific patient needs or preferences.
Development of Biosimilars and Generics
As patents for branded DPP-4 inhibitors begin to expire, there is an opportunity for the development and commercialization of biosimilars and generic versions of these medications. The introduction of biosimilars and generics can increase affordability and accessibility, particularly in markets where cost is a significant barrier to treatment.
The availability of more affordable alternatives can expand the patient pool and drive market growth, especially in emerging economies where healthcare costs are a concern. However, it is crucial for biosimilars and generics to demonstrate bioequivalence and meet stringent regulatory standards to ensure safety and efficacy.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
Advancements in genomics and personalized medicine offer the opportunity to tailor DPP-4 inhibitor therapy based on individual patient characteristics. By identifying genetic variations or biomarkers that influence drug response, it may be possible to optimize treatment regimens and maximize therapeutic outcomes.
Personalized medicine approaches could enhance the efficacy and safety of DPP-4 inhibitors, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs associated with adverse events or treatment failures. This opportunity aligns with the broader trend of precision medicine in healthcare and could differentiate DPP-4 inhibitors in the market.
Market Trends:
Development of Combination Therapies
A significant trend in the DPP-4 inhibitors market is the development of combination therapies that incorporate these medications with other antidiabetic agents. Combination therapies offer improved glycemic control by targeting multiple pathways involved in glucose regulation, while also providing convenience for patients by reducing pill burden.
Several pharmaceutical companies have introduced fixed-dose combination products that combine DPP-4 inhibitors with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, or GLP-1 agonists. Examples include Qtern (dapagliflozin and saxagliptin) by AstraZeneca and Trijardy XR (empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin) by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes
With the increasing recognition of the link between type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, there is a growing trend among pharmaceutical companies to evaluate the cardiovascular safety and potential benefits of DPP-4 inhibitors. Several large-scale clinical trials have been conducted to assess the cardiovascular outcomes of these medications.
The findings from these studies have influenced treatment guidelines and regulatory decisions, shaping the positioning and adoption of DPP-4 inhibitors in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
Adoption of Real-World Evidence
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly relying on real-world evidence (RWE) to complement traditional clinical trial data and gain insights into the effectiveness, safety, and patient adherence of DPP-4 inhibitors in real-world settings. RWE can be derived from electronic health records, patient registries, claims data, and other sources.
The adoption of RWE can inform drug development, regulatory decisions, and clinical practice guidelines, ultimately driving the appropriate use and market growth of DPP-4 inhibitors. Additionally, RWE can help identify patient subgroups that may benefit most from these medications, facilitating personalized treatment approaches.
Emphasis on Patient-Centric Approaches
There is a growing trend towards patient-centric approaches in the development and commercialization of DPP-4 inhibitors. Pharmaceutical companies are focusing on improving patient adherence, convenience, and overall experience with these medications.
Efforts include the development of once-weekly or once-monthly formulations, fixed-dose combination products to reduce pill burden, and digital health solutions that support patient education and monitoring. Additionally, companies are exploring patient support programs and partnerships with healthcare providers to enhance disease management and improve treatment outcomes.
Market Restraints:
Patent Expiries and Generic Competition
The DPP-4 inhibitors market faces the challenge of patent expiries for several branded medications, leading to increased generic competition. As patents expire, generic manufacturers can introduce lower-cost alternatives, exerting pricing pressures on branded products and potentially eroding market share.
For example, the patent for Merck's Januvia (sitagliptin), one of the first DPP-4 inhibitors to enter the market, expired in 2022, allowing generic versions to be launched. Similarly, the patents for other widely prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors, such as Onglyza (saxagliptin) and Tradjenta (linagliptin), are set to expire in the coming years.
While generic competition can enhance affordability and accessibility, it can also lead to reduced revenue streams for pharmaceutical companies, potentially impacting their ability to invest in research and development for innovative DPP-4 inhibitors or combination therapies.
Stringent Regulatory Requirements
The development and approval of new DPP-4 inhibitors or combination therapies are subject to stringent regulatory requirements imposed by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). These regulatory bodies have stringent standards for demonstrating the safety, efficacy, and quality of new medications.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape can be time-consuming and resource-intensive for pharmaceutical companies. Rigorous clinical trials and extensive documentation are required to gain regulatory approval, which can delay the market entry of new DPP-4 inhibitors or combination therapies.
Furthermore, any safety concerns or adverse event reports can prompt regulatory agencies to impose additional requirements or restrictions, potentially impacting the market growth and adoption of these medications.
Reimbursement Challenges
Access to DPP-4 inhibitors can be hindered by reimbursement challenges, particularly in markets with stringent cost-containment measures or limited healthcare resources. Payers, such as government healthcare programs and private insurance providers, may impose restrictions or require prior authorizations to manage the costs associated with these medications.
Reimbursement decisions are often based on factors such as clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and budget impact analyses. If DPP-4 inhibitors are perceived as having limited cost-effectiveness compared to alternative treatments or are deemed too expensive, payers may limit coverage or impose high co-payments, creating barriers to patient access.
Additionally, differences in reimbursement policies across regions or countries can lead to disparities in the availability and affordability of DPP-4 inhibitors, potentially hindering market growth in certain geographic areas.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Involved Company |
|
Launched Qtern, a combination therapy of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin, in April 2022 for type 2 diabetes. |
AstraZeneca |
|
Received FDA approval for Quvempid, a novel DPP-4 inhibitor, in February 2023, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. |
Novartis |
|
Announced positive results from Phase 3 trial of its investigational DPP-4 inhibitor, omarigliptin, in March 2021. |
Merck & Co. |
|
Product Launch |
Company Name |
|
Launched Steglujan, a combination of ertugliflozin and sitagliptin, in December 2022 for type 2 diabetes. |
Merck & Co. |
|
Received FDA approval for Trijardy XR, a triple combination therapy, in January 2020 for type 2 diabetes. |
Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly |
|
Launched Glyxambi, a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin, in August 2021 for type 2 diabetes. |
Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly |
|
Merger/Acquisition |
Involved Companies |
|
Acquired Arxxant, a company developing a novel DPP-4 inhibitor, in November 2022 for $1.6 billion. |
AstraZeneca, Arxxant |
|
Acquired Akcea Therapeutics, a company with a pipeline of cardiometabolic drugs, in October 2020 for $4 billion. |
Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Akcea Therapeutics |
|
Acquired the global rights to Marizev (omarigliptin) from Merck & Co. in January 2021 for $300 million. |
Novartis, Merck & Co. |
Market Regional Insights:
The Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market is witnessing significant growth across various regions, driven by the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes and the adoption of these medications as part of combination therapy regimens.
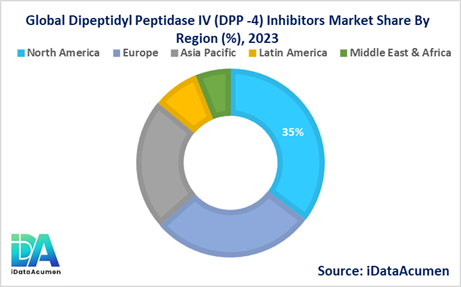
- North America is expected to be the largest market for the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market during the forecast period, accounting for over 35.2% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the high prevalence of type 2 diabetes, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and favorable reimbursement policies.
- The European market is expected to be the second-largest market for the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market, accounting for over 28.1% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market is attributed to the increasing adoption of these medications as part of diabetes management guidelines and the availability of advanced healthcare facilities.
- The Asia-Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market, with a CAGR of over 22.5% during the forecast period by 2024. The growth of the market in the Asia-Pacific region is attributed to the rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing adoption of Western lifestyles, contributing to a higher disease burden, with a market share of 14.8%.
Market Segmentation:
- By Drug Class
- Sitagliptin
- Saxagliptin
- Linagliptin
- Alogliptin
- Vildagliptin
- Others (Gemigliptin, Evogliptin, Teneligliptin)
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others (Transdermal, Nasal)
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others (Clinics, Research Institutes)
- By Disease Indication
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Others (Obesity, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- By Patient Demographics
- Geriatric Population
- Adults
- Pediatrics
- By End-User
- Hospitals
- Homecare
- Specialty Clinics
- Others (Research Institutes, Academic Institutions)
- By Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Market Segment Analysis:
- By Drug Class: The sitagliptin segment is expected to maintain its leading position and hold the largest market share in 2024, owing to its widespread adoption, availability of generic versions, and cost-effectiveness. However, the linagliptin segment is projected to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by its favorable safety profile and once-daily dosing regimen, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region.
- By Route of Administration: The oral segment is anticipated to dominate the market in 2024 and continue its growth trajectory, as most DPP-4 inhibitors are available in oral formulations. However, the parenteral segment is expected to exhibit a higher CAGR due to the development of injectable formulations, offering improved patient compliance and convenience.
- By Distribution Channel: The hospital pharmacies segment is likely to remain the largest in 2024, as these facilities are the primary point of care for diabetes management. However, the online pharmacies segment is projected to experience the highest CAGR, driven by the growing trend of e-commerce and the convenience of home delivery, particularly in urban areas.
It is important to note that these projections may vary based on the specific region or market under consideration, as factors such as healthcare infrastructure, reimbursement policies, and disease prevalence can influence segment growth.
Top companies in the Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-4) Inhibitors Market
- Merck & Co.
- Novartis AG
- AstraZeneca
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Bayer AG
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- AbbVie Inc.
- Mylan N.V.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd.
- Cipla Inc.
- Lupin Limited
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.