The Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE) Market is poised for significant growth, with projections indicating a leap from its 2023 valuation of US$ 1.2 billion to a substantial US$ 1.7 billion by the year 2030. This growth is anticipated to materialize at a steady Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.9% over the forecast period spanning from 2023 to 2030.
CLE encompasses a cluster of autoimmune skin disorders characterized by an aberrant immune system response directed against skin tissues and cells. The consequence of this immune dysregulation is the development of inflammatory rashes and lesions, primarily afflicting sun-exposed areas of the skin. Driving this market's expansion are factors such as the escalating prevalence of autoimmune disorders and intensified research and development endeavors aimed at pioneering novel therapeutic solutions.

The segmentation of the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market comprises distinct categories based on type, treatment, end-user, distribution channel, and geographic region. Within the realm of CLE types, discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) emerges as the most prevalent subtype, constituting nearly 80% of all CLE cases. This predominance of DLE is primarily attributed to its widespread occurrence among affected individuals, signifying a considerable portion of the market share.
In January 2023, Pfizer received the US FDA approval for ritlecitinib (Minjuv) for treating adults with discoid lupus erythematosus. The approval provides the first approved treatment option for DLE in the last 70 years.
Epidemiology Insights:
- The prevalence of cutaneous lupus erythematosus is high across North America and Europe owing to the higher incidence of autoimmune disorders in these regions.
- The prevalence is rising globally due to factors like increasing exposure to ultraviolet radiation, air pollution, smoking, infections, and vitamin D deficiency.
- As per estimates, the prevalence of CLE in the US is around 1 in 250 adults with nearly 200,000 Americans living with some form of CLE. The prevalence in Europe is around 40 cases per 100,000 population.
- The incidence rates are lower in Asian countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan compared to western countries. However, the prevalence is rising in Asia Pacific due to westernization of lifestyles.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common subtype with incidence ranging from 20-70 cases per 100,000 population across major markets.
- CLE is still considered an orphan disease with high unmet need for effective therapies.
Market Landscape:
- There is a high unmet clinical need for effective therapeutic options for refractory and rare subtypes of CLE such as lupus panniculitis and chilblain lupus.
- The current treatment options include corticosteroids, antimalarial drugs, immunosuppressants, biologics like belimumab, and recently approved JAK inhibitors.
- Emerging therapies in the pipeline include antibodies targeting immune pathways like B cells, IL-12/23, IL-17, JAK-STAT.
- Advanced skin-targeted drug delivery systems are being developed to improve efficacy and minimize side effects.
- Cell-based therapies like mesenchymal stem cells and PRP are being evaluated for treatment-resistant CLE.
- The CLE market has a mix of branded, generic, and biosimilar manufacturers. Brands still dominate owing to patent exclusivity.
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Drivers:
Increasing prevalence of autoimmune disorders
The rising prevalence of autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and others is a major factor driving the growth of the cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) market. Autoimmune conditions often co-occur with CLE. As per estimates, around 20% of people with systemic lupus erythematosus develop some form of CLE. With autoimmune diseases on the rise globally, the patient pool for CLE is expanding, creating growth opportunities for novel therapies. For instance, the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis is rising steadily across developed countries. Environmental factors like smoking, infections, hormonal changes are contributing to the increasing incidence of autoimmunity worldwide. The growing patient base and unmet need are encouraging investments in R&D for new CLE treatments.
Increasing research and development activities
The cutaneous lupus erythematosus pipeline continues to expand with biopharmaceutical companies increasingly focusing on R&D for new targeted CLE therapies. Advances in the understanding of the immunological pathways involved in CLE pathogenesis have enabled targeted drug development. For example, the role of cytokines like IL-17 and JAK-STAT signaling in promoting skin inflammation and damage has led to novel drugs like JAK inhibitors. The US FDA approved Incyte’s JAK inhibitor Opzelura cream for mild to moderate DLE in 2022. Several monoclonal antibodies targeting immune cells and pathways are in clinical trials such as anifrolumab, filgotinib, ustekinumab. Further, technological advances are aiding the development of novel delivery systems like nanoparticles, liposomes for better skin penetration. The high unmet need and commercial potential are incentivizing investments in R&D, thereby driving the CLE therapeutics market.
Favorable government initiatives
The enactment of legislations like the Orphan Drug Act provides incentives to encourage rare disease R&D including therapies for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Orphan status for CLE allows seven years of marketing exclusivity and other benefits like tax credits which help offset development costs. For instance, Incyte’s Opzelura received orphan drug designation which supported its clinical development. The 21st Century Cures Act is also aiding the advancement of new treatments by facilitating faster regulatory approvals. Further, increased funding by organizations like the NIH helps accelerate research. Government support through special designations and research grants incentivize biopharma innovation, thereby catalyzing the cutaneous lupus erythematosus market growth.
Improved diagnosis and disease awareness
Advances in diagnostic techniques are aiding the timely and accurate diagnosis of CLE, leading to increased disease detection. Novel imaging modalities like reflectance confocal microscopy allow rapid visualization of CLE skin lesions at cellular-level resolution. High throughput genomic analysis helps identify gene expression patterns, autoantibody profiles to diagnose CLE subtypes. The uptake of AI and machine learning is further improving diagnosis through automated image analysis. Multi-disciplinary care centers dedicated to CLE diagnosis and management are being established. Awareness initiatives through organizations like the APPLEP increase disease awareness among patients and physicians. Diagnostic improvements are facilitating early intervention and boosting the addressable patient pool for CLE therapies.
|
Key Insights |
Description |
|
The market size in 2023 |
US$ 1.2 Bn |
|
CAGR (2023 - 2030) |
4.9% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2030 |
US$ 1.7 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2021 |
|
Historical data |
2017-2020 |
|
Forecast period |
2023-2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
By Treatment: Corticosteroids, Antimalarial agents, Immunosuppressive agents, Monoclonal antibodies, JAK inhibitors, Others By Distribution Channel: Hospital pharmacies, Retail pharmacies, Online pharmacies, Dermatology clinics, Others |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Pfizer, Merck, Abbvie, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Roche, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Amgen, GSK, Eli Lilly, Bayer, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Biogen and Allergan |
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Opportunities:
Large unmet need for rare CLE subtypes
There is a particularly high unmet need for effective therapies for rare cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes such as lupus panniculitis, chilblain lupus, and intermittent CLE. The underlying disease mechanisms of these subtypes are still poorly understood. Their lower prevalence offers limited commercial incentives for targeted R&D by biopharma companies. However, the substantial morbidity and diminished quality of life associated with these rare CLE subtypes represent a major opportunity for developers of novel treatments. Companies that invest in orphan drug development and utilize regulatory incentives can realize significant first-mover advantage. For instance, skin-targeted drugs, next-gen biologics inhibiting specific cytokines implicated in rare CLE could open up substantial market opportunities.
Leveraging advanced therapies
The integration of advanced modalities like gene therapy, cell therapy, RNA interference holds potential for better CLE treatment. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 could correct disease-associated genetic mutations. Mesenchymal stem cells, PRP therapy may find use in refractory CLE cases owing to their immunomodulatory effects. siRNA technology enables specific silencing of aberrantly expressed genes or inflammatory mediators involved in CLE pathophysiology. Precision delivery systems like dissolving microneedle patches, lipid nanoparticles can improve topical RNAi therapy outcomes. Biopharma players investing in these emerging platforms early-on could establish market leadership in advanced CLE therapies.
Strategic collaborations and partnerships
Collaborations between pharmaceutical, biotech, and academic entities to combine complementary expertise can accelerate cutaneous lupus erythematosus drug development. Academic researchers possess extensive knowledge on disease biology and can identify novel targets. Biotech firms specialize in translating research into drug candidates leveraging technology platforms. Pharmaceutical majors have the resources and experience to successfully steer clinical development and commercialization. Cross-industry and public-private strategic partnerships take advantage of complementary strengths at various stages of the therapy lifecycle. Open innovation models enhance the knowledge, resource, and risk-sharing - vital for rare disease R&D like CLE.
Expansion in emerging markets
The emerging markets represent an area of strong growth potential for cutaneous lupus erythematosus therapies owing to rising disposable incomes, increasing healthcare spending, and improving infrastructure. Developing economies like China, India, Brazil are witnessing a steady increase in autoimmune disorder prevalence spurred by urbanization and changing lifestyles. Localized environmental and genetic factors may be implicated in increased CLE incidence in certain developing regions. Companies that make early investments and develop a strong regional presence are well-positioned to benefit from the opportunities offered by emerging pharmerging markets.
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Trends:
Combination therapy approaches
The development of combination regimens using drugs with complementary mechanisms of action is an emerging trend in cutaneous lupus erythematosus management. Combination therapy can offer synergistic effects, allow lower dosages of individual agents and reduce side effects. For instance, triple therapy combining hydroxychloroquine, quinacrine, and corticosteroids is being evaluated for refractory CLE. Dual JAK + IRAK4 inhibition displayed potential in preclinical lupus studies. Topical-systemic combinations like ritlecitinib cream with plaquenil are also being assessed. Combination approaches leveraging novel MOAs like biologics, small molecules seem promising for improved, personalized CLE treatment.
Stratification and targeted treatment
Stratification and subtyping of cutaneous lupus erythematosus patients using clinical markers, immunological profiling, genetics and AI are gaining traction. This allows treatment personalization based on the molecular signature and enhances outcomes. For example, anifrolumab works better in patients with high interferon gene expression. Filgotinib may be more effective for pedal lupus owing to localized IL-17 involvement. Genetic screening helps predict drug metabolism patterns and adverse effect susceptibility. Diagnostic improvements like proteomics and transcriptomics facilitate biomarker identification for optimal therapy selection. Patient stratification is enabling precision medicine approaches for CLE.
Specialized drug delivery systems
Novel drug delivery systems like nanoparticles, liposomes, microemulsions are being leveraged to enhance topical therapy outcomes in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. These systems allow sustained drug release over a prolonged period to minimize repeated application. They protect the drug payload and increase its localized concentration in the skin layers. Advanced delivery systems enhance the stability, penetration, tolerability of encapsulated drugs like steroids, antimalarials, siRNAs. For instance, a transfersomal gel formulation of methotrexate demonstrated superior skin retention. Specialized delivery platforms offer an attractive strategy to overcome the challenges of topical CLE therapy.
Digital health integration
Digital health integration is rising in cutaneous lupus erythematosus management through mobile apps for tracking symptoms, AI-enabled medical devices for early diagnosis, telemedicine platforms for remote specialist consultations. Mobile apps like Spot My UV allow logging of CLE flare-ups and relevant contextual data. AI techniques analyzing patient selfies can potentially detect early lesions. Remote patient monitoring and telehealth improve access and adherence. Adoption of EHRs and health informatics enhances data-driven research. Digital integration provides opportunities to enhance care coordination, patient engagement and outcomes in CLE.
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Restraints:
Lack of standardized diagnosis and care guidelines
The lack of consensus on standardized guidelines for diagnosis and management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus subtypes is a key factor restricting market growth. Considerable overlap exists between clinical manifestations of DLE, SCLE, ACLE which complicates diagnosis. There is no definitive test to distinguish CLE subtypes. Variability in diagnostic criteria between experts is common. Further, no universally accepted standard of care exists for CLE treatment due to the heterogeneous, unpredictable disease course. This results in variable clinical outcomes across practitioners. The ambiguities in diagnosis and optimal protocols hamper patient care and limit the eligible pool for novel CLE therapies. Published expert recommendations can aid physicians and improve patient journeys.
High costs of novel biologics and small molecules
Novel targeted therapies like monoclonal antibodies and kinase inhibitors which are emerging for cutaneous lupus erythematosus treatment come at high costs and may hinder uptake. For instance, the annual cost of the newly approved JAK inhibitor Opzelura cream is around $64,000 which increases the economic burden. Most CLE patients require lifelong therapy. Pricing pressures are more significant in emerging economies where reimbursement is limited. Given the chronic nature of CLE, more economical treatment alternatives may be preferred over costly novel biologics or small molecules by patients and payers alike. Companies need to consider affordability along with efficacy while developing new CLE drugs.
Probable adverse effects
The probable side effects of investigational cutaneous lupus erythematosus therapies can affect their uptake following commercial launch. Most novel drugs like JAK inhibitors, MEK inhibitors, biologics have an immunosuppressive action which increases infection risks. For example, Opzelura usage has been linked with herpetic infections in trials. Other common side effects include GI disturbances, respiratory infections, alopecia, rashes, etc. associated with novel MOAs. These may outweigh benefits in mild CLE. Strict pharmacovigilance and post-marketing surveillance are critical to monitor long-term safety. Demonstrating a favorable benefit-risk profile through robust late-phase trials can help gain confidence among prescribers and patients.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Involved Company |
|
In January 2023, Pfizer received the US FDA approval for ritlecitinib (Minjuv) for treating moderate to severe discoid lupus erythematosus in adults. Minjuv became the first FDA-approved treatment specifically for DLE in nearly 70 years. |
Pfizer |
|
In April 2022, Incyte announced the US FDA approval of Opzelura cream for the topical short-term and non-continuous chronic treatment of mild to moderate discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) in adult patients. |
Incyte Corporation |
|
In June 2021, Lilly launched Olumiant (baricitinib) after receiving the US FDA approval for treating adult patients with discoid lupus erythematosus. |
Eli Lilly |
|
Merger/Acquisition |
Involved Company |
|
In June 2020, AbbVie completed the acquisition of Allergan in a $63 billion deal. The acquisition expanded and diversified AbbVie's product portfolio including Botox which is being studied for managing cutaneous lupus erythematosus. |
AbbVie and Allergan |
|
In July 2019, Takeda Pharmaceutical completed its acquisition of Shire Plc for $62 billion. The deal strengthened Takeda's immunology drug portfolio. |
Takeda and Shire |
|
In April 2018, Novartis acquired AveXis for $8.7 billion in cash. The deal added gene therapy technology platform to Novartis' portfolio which can be leveraged for developing therapies for cutaneous lupus. |
Novartis and AveXis |
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Regional Insights:
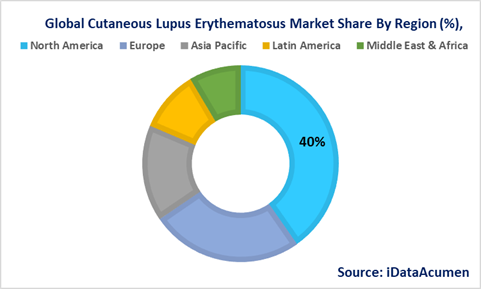
North America is poised to exert its dominance over the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE) Market during the forecast period, with expectations to commandeer more than 40% of the market share in 2023. This substantial share can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including the high prevalence of CLE within the region, the presence of key industry players, and the expeditious approval of novel drugs. North America's healthcare landscape is marked by a robust infrastructure and significant research and development efforts, fostering an environment conducive to CLE market growth. Additionally, early approvals of groundbreaking treatments underscore the region's commitment to addressing the unmet medical needs of CLE patients.
Europe is poised to follow as the second-largest market, with projections indicating it will hold over 25% of the market share in 2023. The growth of the CLE market in Europe is propelled by increased investments in research and development, with several leading pharmaceutical companies headquartered in the region. These entities are dedicated to advancing innovative therapies and diagnostic tools, contributing to the market's expansion. Europe's healthcare ecosystem, characterized by its strong regulatory framework and access to advanced healthcare facilities, further bolsters its standing in the CLE market.
The Asia Pacific region is poised to witness the most rapid growth in the CLE market, projecting a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) exceeding 6% between 2023 and 2030. A convergence of factors fuels this growth, including a rising prevalence of CLE, increasing disposable incomes among the population, and substantial improvements in healthcare infrastructure. As awareness about CLE and its management grows, the Asia Pacific region is emerging as a significant player in the global CLE market landscape. It is predicted to exhibit the 15.8% growth among all regions, making it a focal point for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers alike.
In addition to the Asia Pacific region, Latin America is expected to experience notable growth with a CAGR of 10.1%, while the Middle East and Africa region is projected to grow at 8.4% during the forecast period. These regions are witnessing an upward trajectory in CLE prevalence, and efforts to enhance healthcare infrastructure and access to treatments are driving market expansion in these areas, albeit at a slightly slower pace compared to the Asia Pacific region.
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market Segmentation:
- By Treatment
- Corticosteroids
- Antimalarial agents
- Immunosuppressive agents
- Monoclonal antibodies
- JAK inhibitors
- Others
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital pharmacies
- Retail pharmacies
- Online pharmacies
- Dermatology clinics
- Others
- By Regions
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- U.K.
- Spain
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
-
- Israel
- South Africa
- North Africa
- Central Africa
- Rest of the Middle East
- North America
Top companies in the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Market
- Pfizer
- Merck
- Abbvie
- Novartis
- Johnson & Johnson
- Roche
- AstraZeneca
- Sanofi
- Amgen
- GSK
- Eli Lilly
- Bayer
- Takeda
- Daiichi Sankyo
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Astellas Pharma
- Gilead Sciences
- Biogen
- Allergan