Market Analysis:
The Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market had an estimated market size worth US$ 120 million in 2023, and it is predicted to reach a global market valuation of US$ 1,896.1 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 41.2% from 2024 to 2031.
Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) inhibitors are a class of drugs that target the CTGF protein, which plays a crucial role in the development of fibrotic diseases. These inhibitors aim to block or reduce the activity of CTGF, thereby potentially preventing or reversing the progression of fibrotic diseases affecting various organs, such as the lungs, liver, kidneys, and skin. By inhibiting CTGF, these drugs can potentially reduce excessive scarring and tissue thickening, improving organ function and patient outcomes.
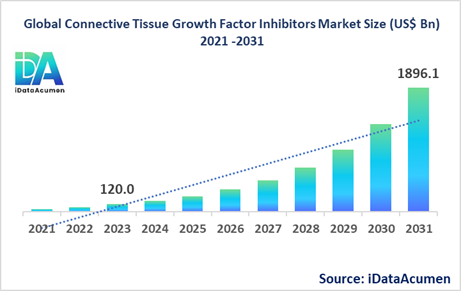
The increasing prevalence of fibrotic diseases and the lack of effective treatments are major drivers for the growth of the CTGF Inhibitors Market.
Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors are a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of fibrotic diseases, a group of conditions characterized by excessive scarring and tissue stiffening.
The Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market is segmented by product type, therapeutic area, and region. By product type, the market is segmented into monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, antisense oligonucleotides, and others (gene therapies, RNAi-based therapies). Monoclonal antibodies are expected to be a significant segment, as several companies are developing monoclonal antibodies targeting CTGF for the treatment of fibrotic diseases. For example, FibroGen's pamrevlumab, a monoclonal antibody against CTGF, is being investigated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and other fibrotic diseases. This segment is growing due to the high specificity and potential effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in targeting CTGF.
Recent examples of product launches in this segment include FibroGen's initiation of a Phase 3 clinical trial for pamrevlumab in IPF patients in March 2023.
Epidemiology Insights:
- The disease burden of fibrotic diseases is significant across major regions, with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) being a major contributor. In the United States, it is estimated that approximately 100,000 people are living with IPF, while in Europe, the prevalence is around 3 cases per 10,000 people.
- Key epidemiological trends and driving factors include the aging population, increased exposure to environmental and occupational risk factors, and improved diagnostic techniques for detecting fibrotic diseases. The prevalence of fibrotic diseases is expected to rise as the population ages and risk factors such as smoking, pollution, and certain medications increase.
- In the United States, the incidence of IPF is estimated to be around 16-18 cases per 100,000 population per year, while in Europe, the incidence ranges from 1.3 to 23 cases per 100,000 population per year.
- As the patient population with fibrotic diseases continues to grow, there is a significant growth opportunity for effective treatments like CTGF inhibitors, which can potentially slow or reverse the progression of these debilitating conditions.
- While fibrotic diseases are not classified as rare diseases individually, they are considered rare when combined, with an estimated prevalence of less than 1 in 2,000 people in the general population.
Market Landscape:
- There are significant unmet needs in the treatment of fibrotic diseases, as currently available therapies primarily focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, but do not target the underlying mechanisms of fibrosis.
- Current treatment options for fibrotic diseases include immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and lung transplantation (for IPF). However, these treatments have limited efficacy and significant side effects.
- Several pharmaceutical companies are developing CTGF inhibitors as potential breakthrough therapies for fibrotic diseases. These include FibroGen's pamrevlumab, Gilead's GB0139, and Biogen's BIIB023, among others.
- CTGF inhibitors represent a promising breakthrough treatment option as they target the root cause of fibrosis by inhibiting the activity of CTGF, a key driver of excessive scarring and tissue stiffening.
- The market for fibrotic disease treatments is currently dominated by branded drug manufacturers, as there are limited generic options available for these complex and rare conditions.
Market Report Scope:
|
Description |
|
|
The market size in 2023 |
US$ 120 Mn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
41.2% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 1,896.1 Mn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Market Drivers:
Increasing Prevalence of Fibrotic Diseases
The rising prevalence of fibrotic diseases is a significant driver for the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market. Fibrotic diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), liver fibrosis, and diabetic kidney disease, are becoming more common due to factors like an aging population, environmental exposures, and the increasing incidence of underlying conditions like diabetes. As the patient population affected by these debilitating conditions grows, the demand for effective treatments like CTGF inhibitors is expected to surge.
Furthermore, the burden of fibrotic diseases is substantial, with IPF alone affecting approximately 3 million people worldwide. This high disease burden underscores the urgent need for novel therapeutic options that can slow or reverse the progression of fibrosis, driving research and development efforts in the CTGF inhibitor space.
Unmet Medical Needs and Lack of Effective Treatments
Current treatment options for fibrotic diseases are limited and primarily focus on managing symptoms or slowing disease progression. However, these treatments often have limited efficacy and significant side effects. This lack of effective treatment options creates a significant unmet medical need, driving the development of CTGF inhibitors as a promising therapeutic approach.
By targeting the root cause of fibrosis, CTGF inhibitors have the potential to provide a more effective and targeted treatment for patients with fibrotic diseases. This unmet medical need has fueled substantial investment and research efforts by pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions to explore the potential of CTGF inhibitors.
Advancements in Diagnostic Techniques
Improvements in diagnostic techniques, such as imaging modalities and biomarkers, have facilitated the early detection and monitoring of fibrotic diseases. As diagnostic capabilities advance, more patients can be identified and treated earlier in the disease progression, increasing the potential patient population for CTGF inhibitors.
Furthermore, the development of accurate diagnostic tools enables better patient stratification and personalized treatment approaches, enhancing the effectiveness of CTGF inhibitors and driving their adoption in clinical practice.
Expanding Target Indications
While CTGF inhibitors are primarily being developed for the treatment of fibrotic diseases affecting organs like the lungs, liver, and kidneys, their potential therapeutic applications are expanding. Researchers are exploring the use of CTGF inhibitors in other conditions involving excessive scarring or tissue remodeling, such as cardiac fibrosis, macular degeneration, and systemic sclerosis.
As the understanding of CTGF's role in various pathological processes deepens, the potential target indications for CTGF inhibitors broaden, creating new market opportunities and driving further research and development in this therapeutic area.
Market Opportunities:
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
The development of CTGF inhibitors presents significant opportunities for strategic collaborations and partnerships between pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and biotechnology firms. These collaborations can leverage the collective expertise, resources, and capabilities of different organizations to accelerate the research, development, and commercialization of CTGF inhibitors.
For example, pharmaceutical companies can partner with academic research institutions to gain access to cutting-edge scientific knowledge and novel therapeutic targets related to CTGF. Conversely, biotechnology firms can collaborate with larger pharmaceutical companies to leverage their expertise in drug development, regulatory affairs, and global commercialization.
Such strategic collaborations can facilitate the sharing of risks, costs, and rewards associated with the development of CTGF inhibitors, ultimately expediting the delivery of these promising therapies to patients.
Combination Therapies
CTGF inhibitors present opportunities for combination therapy approaches, where they are used in conjunction with existing treatments or other novel therapies targeting different aspects of fibrotic diseases. By combining CTGF inhibitors with complementary therapeutic modalities, synergistic effects may be achieved, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy and improving patient outcomes.
For instance, CTGF inhibitors could be combined with anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory agents to address the complex pathways involved in fibrotic diseases. Additionally, combining CTGF inhibitors with antioxidant or anti-fibrotic therapies may provide a multi-pronged approach to tackle the various mechanisms contributing to tissue scarring and organ dysfunction.
Personalized Medicine and Biomarker-Driven Approaches
The development of CTGF inhibitors presents opportunities for personalized medicine approaches and biomarker-driven treatment strategies. By identifying specific biomarkers or genetic signatures associated with CTGF expression or fibrotic disease progression, patients can be stratified and targeted with tailored CTGF inhibitor therapies.
This personalized approach can potentially improve treatment efficacy, minimize adverse effects, and optimize patient outcomes by ensuring that the right therapy is provided to the right patient at the appropriate time. Moreover, biomarker-driven approaches can facilitate the development of companion diagnostics, further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of CTGF inhibitor therapies.
Emerging Markets and Global Accessibility
As the burden of fibrotic diseases increases globally, there is a significant opportunity for CTGF inhibitors to address unmet medical needs in emerging markets. These markets represent a substantial patient population and a growing demand for innovative therapies.
By developing cost-effective and accessible CTGF inhibitors, pharmaceutical companies can tap into these emerging markets and expand their global reach. Collaborations with local partners, technology transfers, and tailored pricing strategies can help overcome barriers to accessibility and ensure that CTGF inhibitors are available to patients in need, regardless of their geographic location or economic status.
Market Trends:
Development of Novel CTGF Inhibitors
One of the key trends in the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market is the ongoing development of novel and innovative CTGF inhibitors. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies are actively exploring different therapeutic modalities, such as monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, antisense oligonucleotides, and gene therapies, to target CTGF effectively.
These novel approaches aim to overcome the limitations of existing therapies and provide more potent, specific, and targeted inhibition of CTGF. For instance, monoclonal antibodies like pamrevlumab are being investigated for their potential to neutralize CTGF activity with high specificity, while small molecule inhibitors offer the advantage of oral administration and potential cost-effectiveness. Recent examples of novel CTGF inhibitors in development include Biogen's antisense oligonucleotide BIIB023 and AstraZeneca's investigational small molecule inhibitor AZD8601.
Expansion of Clinical Trial Pipelines
Another notable trend in the CTGF Inhibitors Market is the expansion of clinical trial pipelines exploring the potential of these therapies across various fibrotic diseases. As the understanding of CTGF's role in fibrosis deepens, companies are actively pursuing clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of CTGF inhibitors in different indications, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), diabetic kidney disease, liver fibrosis, and systemic sclerosis.
This trend is driven by the promising preclinical and early-stage clinical data demonstrating the potential of CTGF inhibitors in slowing or reversing the progression of fibrosis. For example, FibroGen recently initiated a Phase 3 clinical trial for pamrevlumab in IPF patients, while Gilead Sciences announced positive results from a Phase 2 study evaluating GB0139 in pancreatic cancer patients with fibrosis.
Emphasis on Biomarker Development and Companion Diagnostics
As the CTGF Inhibitors Market evolves, there is an increasing emphasis on the development of biomarkers and companion diagnostics. Biomarkers can aid in the early detection and monitoring of fibrotic diseases, enabling timely intervention and personalized treatment strategies.
Moreover, the identification of specific biomarkers associated with CTGF expression or fibrotic disease progression can facilitate the development of companion diagnostics. These companion diagnostics can be used to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from CTGF inhibitor therapies, improving treatment outcomes and optimizing the use of these targeted therapies. Recently, Roche launched the Elecsys® CTGF immunoassay, a diagnostic test designed to measure CTGF levels in patients with fibrotic diseases, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of fibrosis progression.
Adoption of Precision Medicine Approaches
In line with the broader trend in healthcare towards precision medicine, the CTGF Inhibitors Market is witnessing the adoption of personalized and targeted treatment approaches. As our understanding of the genetic and molecular underpinnings of fibrotic diseases deepens, there is a growing recognition of the heterogeneity within patient populations.
Precision medicine approaches aim to tailor CTGF inhibitor therapies based on individual patient characteristics, such as genetic profiles, biomarker expression, and disease subtype. This personalized approach can potentially improve treatment efficacy, minimize adverse effects, and optimize patient outcomes by ensuring that the right therapy is provided to the right patient at the appropriate time. Companies like Merck & Co. are exploring their investigational CTGF inhibitor MK-7264 in a biomarker-driven Phase 2 trial for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and liver fibrosis.
Market Restraints:
High Development Costs and Risks
The development of CTGF inhibitors is a complex and resource-intensive process, presenting a significant restraint to the growth of this market. The research and development of novel therapeutic modalities, such as monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, and gene therapies, requires substantial financial investments and long-term commitments.
Moreover, the process of drug development is inherently risky, with a high attrition rate as potential candidates navigate through preclinical and clinical testing phases. Failures in clinical trials or during regulatory approval processes can result in significant financial losses and setbacks for companies involved in the development of CTGF inhibitors. These high costs and risks associated with drug development can potentially discourage investment and hinder the progress of new CTGF inhibitor therapies.
Stringent Regulatory Approval Processes
The regulatory approval processes for CTGF inhibitors, like other novel therapeutic modalities, are rigorous and stringent. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), require extensive clinical data demonstrating the safety and efficacy of these therapies before granting approval for marketing and commercial use.
The complex nature of fibrotic diseases and the potential for CTGF inhibitors to impact various biological pathways and organ systems can raise concerns regarding safety and off-target effects. Navigating these regulatory hurdles can be challenging, time-consuming, and resource-intensive, potentially slowing down the entry of CTGF inhibitors into the market and restraining the growth of this therapeutic area.
Potential Side Effects and Toxicity Concerns
While CTGF inhibitors hold promise as targeted therapies for fibrotic diseases, there are concerns regarding potential side effects and toxicity. CTGF plays a role in various physiological processes, and its inhibition may have unintended consequences or off-target effects on other biological pathways.
For example, CTGF is involved in wound healing and tissue repair processes, and its inhibition could potentially impair these functions, leading to adverse effects. Additionally, long-term inhibition of CTGF may have implications on tissue homeostasis and regeneration, raising safety concerns.
These potential side effects and toxicity issues may require careful monitoring and management strategies, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of CTGF inhibitors until their safety profiles are well-established through extensive clinical studies and post-marketing surveillance.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Involved Company |
|
In March 2023, FibroGen announced the initiation of the ZEPHYRUS Phase 3 clinical trial evaluating pamrevlumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CTGF, for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This trial aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pamrevlumab in slowing disease progression in IPF patients. |
FibroGen, Inc. |
|
In September 2022, Gilead Sciences announced positive results from the Phase 2 MYLORD study evaluating GB0139, a monoclonal antibody against CTGF, in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. The study met its primary endpoint, showing a significant improvement in overall survival. |
Gilead Sciences, Inc. |
|
In June 2021, Biogen announced the initiation of a Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating BIIB023, an antisense oligonucleotide targeting CTGF, in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The study aims to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of BIIB023 in slowing disease progression. |
Biogen Inc. |
|
Product Launch |
Company Name |
|
In January 2023, Roche announced the launch of a new diagnostic test, the Elecsys® CTGF immunoassay, designed to measure CTGF levels in patients with fibrotic diseases. This test aims to aid in the early detection and monitoring of fibrosis progression. |
Roche Holding AG |
|
In August 2022, Merck & Co. announced the launch of their investigational CTGF inhibitor, MK-7264, in a Phase 2 clinical trial for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and liver fibrosis. The trial aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MK-7264 in slowing or reversing liver fibrosis. |
Merck & Co., Inc. |
|
In May 2021, AstraZeneca announced the initiation of a Phase 1 clinical trial for their investigational CTGF inhibitor, AZD8601, in healthy volunteers. This trial is the first step in evaluating the safety and tolerability of AZD8601 for potential use in the treatment of fibrotic diseases. |
AstraZeneca PLC |
|
Merger/Acquisition |
Involved Companies |
|
In November 2022, FibroGen announced the acquisition of Pamrevlumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CTGF, from Radrennor Biopharma for $25 million upfront and additional milestone payments. This acquisition strengthens FibroGen's pipeline in the CTGF inhibitor space. |
FibroGen, Inc. and Radrennor Biopharma |
|
In July 2021, Gilead Sciences announced the acquisition of Novartis' exclusive rights to develop and commercialize novel CTGF inhibitors, including the investigational compound GB0139, for $275 million upfront and potential milestone payments. |
Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Novartis AG |
|
In January 2020, Biogen announced the acquisition of Nightstar Therapeutics, a gene therapy company, for $800 million. This acquisition expanded Biogen's pipeline to include CTGF-targeting gene therapies for the treatment of fibrotic diseases. |
Biogen Inc. and Nightstar Therapeutics |
Market Regional Insights:
The Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market is segmented across several regions, with varying growth prospects and market dynamics. North America is expected to be the largest market for CTGF inhibitors, followed by Europe and the Asia-Pacific region.
- North America is expected to be the largest market for the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market during the forecast period, accounting for over 42.5% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the increasing prevalence of fibrotic diseases, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of major pharmaceutical companies actively involved in the development of CTGF inhibitors.
- Europe is expected to be the second-largest market for the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market, accounting for over 30.2% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in Europe is driven by the high disease burden of fibrotic conditions, favorable government initiatives for rare disease research, and the presence of leading pharmaceutical companies exploring CTGF inhibitors.
- The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market, with a CAGR of over 18.7% during the forecast period. The growth of the market in the Asia-Pacific region is attributed to the rising prevalence of fibrotic diseases, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing focus on developing novel therapeutics in emerging economies like China and India.
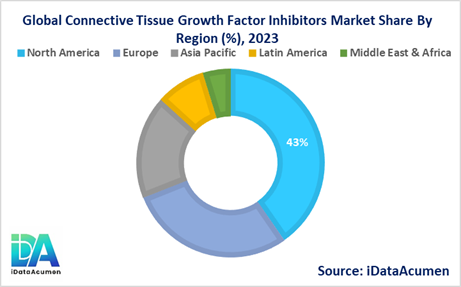
Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Small Molecule Inhibitors
- Antisense Oligonucleotides
- Others (Gene Therapies, RNAi-based therapies)
- By Therapeutic Area
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
- Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Liver Fibrosis
- Systemic Sclerosis
- Cardiac Fibrosis
- Others (Skin Fibrosis, Macular Degeneration)
- By Route of Administration
- Intravenous
- Oral
- Subcutaneous
- Others (Intravitreal, Topical)
- By Mechanism of Action
- CTGF Inhibition
- TGF-beta Inhibition
- Integrin Inhibition
- Others (Oxidative Stress Inhibition, Inflammatory Pathway Inhibition)
- By End-User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Research Institutes
- Others (Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Home Healthcare)
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others (Direct Tenders, Specialty Distributors)
- By Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Segment Analysis:
- By Product Type:
- The monoclonal antibodies segment is projected to experience significant growth in regions like North America and Europe, driven by the development of several promising CTGF-targeting monoclonal antibodies for various fibrotic diseases. This segment is expected to have a CAGR of around 45% during the forecast period and a market size of approximately $900 million by 2030.
- The small molecule inhibitors segment is anticipated to grow rapidly in the Asia-Pacific region, where the market for cost-effective treatments is substantial. This segment may have a CAGR of around 40% and a market size of $500 million by 2030.
- By Therapeutic Area:
- The idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) segment is expected to be the largest in 2024, with a market size of around $400 million, driven by the high prevalence of IPF and the urgent need for effective treatments.
- The diabetic kidney disease segment is projected to be the second-largest in 2024, with a market size of approximately $300 million, as the prevalence of diabetes and its associated complications continues to rise globally.
Top companies in the Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Inhibitors Market
- FibroGen, Inc.
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Biogen Inc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Roche Holding AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- Sanofi S.A.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Bayer AG
- Eli Lilly and Company
- AbbVie Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Amgen Inc.
- Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited
- Eisai Co., Ltd.