A Comprehensive Analysis:
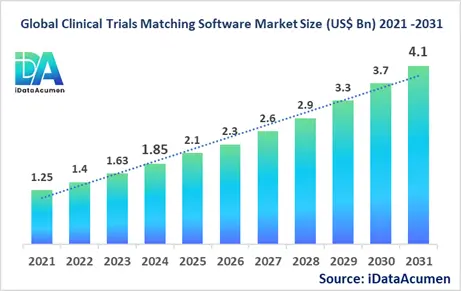
The Clinical Trials Matching Software Market has emerged as a crucial segment within the healthcare technology sector, demonstrating significant growth and potential. In 2024, the market size was estimated at US$ 1.85 billion, and it is projected to reach a global valuation of US$ 4.1 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 12.15% from 2024 to 2031. This robust growth trajectory underscores the increasing importance and adoption of clinical trials matching software across the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries.
Clinical trials matching software is a sophisticated technological solution designed to streamline and optimize the process of connecting potential participants with appropriate clinical trials. This innovative tool leverages advanced algorithms, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics to analyze vast amounts of patient data and trial criteria, facilitating more efficient and accurate matching between researchers and suitable study candidates. The software's primary advantages include accelerating the recruitment process, reducing costs associated with patient identification and enrollment, enhancing the diversity of trial participants, and ultimately speeding up the drug development pipeline.
Key drivers propelling the market's growth include the rising complexity of clinical trials, increasing R&D expenditure in the pharmaceutical sector, and a growing emphasis on patient-centric trial designs. Additionally, the global push towards precision medicine and the need for more efficient trial recruitment processes in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic have further accelerated market expansion.
The Clinical Trials Matching Software Market is segmented by deployment model, end-user, functionality, clinical trial phase, therapeutic area, organization size, component, and region. By deployment model, the market is segmented into cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid solutions. The cloud-based segment is experiencing significant growth due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to facilitate real-time data access and collaboration among stakeholders across different geographical locations.
A notable example of technological advancement in this sector is the launch of IBM Watson Health's IBM Study Advance in September 2020. This AI-powered solution is designed to optimize clinical trial protocol design by analyzing real-world data and previous study protocols, potentially reducing amendments and accelerating the study start-up process.
Epidemiological Insights:
While clinical trials matching software is not directly related to a specific disease, its application spans across various therapeutic areas and has significant implications for epidemiological research and patient recruitment. Understanding the epidemiological landscape is crucial for the development and implementation of effective clinical trials matching software.
The disease burden varies across major regions, with North America, Europe, and parts of Asia Pacific experiencing a higher prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes. For instance, according to the American Cancer Society, there were an estimated 1.9 million new cancer cases in the United States in 2023 alone. In Europe, cardiovascular diseases account for 45% of all deaths, as reported by the European Heart Network.
Key epidemiological trends driving the need for advanced clinical trials matching software include:
- Aging populations in developed countries, leading to an increase in age-related diseases.
- Rising prevalence of chronic diseases globally, particularly in emerging economies.
- Growing awareness and diagnosis of rare diseases, necessitating more targeted recruitment strategies.
- Shift towards precision medicine, requiring more specific patient profiling for trials.
In major markets such as the US, EU5 (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK), and Japan, there's a trend towards increasing incidence of complex diseases that require innovative treatment approaches. For example, the Alzheimer's Association reports that 6.7 million Americans aged 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's in 2023, a number expected to grow to 13.8 million by 2060.
The growth opportunities in the clinical trials matching software market are closely tied to these epidemiological trends. As patient populations for certain diseases increase or become more specifically defined, there's a greater need for sophisticated matching technologies. This is particularly true for rare diseases, where identifying eligible patients can be extremely challenging. The global rare disease population is estimated to be around 350 million, according to the World Health Organization, presenting a significant opportunity for clinical trials matching software to facilitate research in this area.
Moreover, the increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies requires more nuanced patient selection criteria, further driving the demand for advanced matching algorithms. This trend is especially prominent in oncology, where biomarker-driven trials are becoming the norm rather than the exception.
Market Landscape:
The Clinical Trials Matching Software Market landscape is characterized by continuous innovation and evolving needs. Several unmet needs persist in the market, driving ongoing research and development:
- Improved accuracy in matching patients to trials, reducing screen failure rates.
- Enhanced integration with diverse data sources, including electronic health records and genomic databases.
- Better support for decentralized and hybrid clinical trials.
- More sophisticated predictive analytics to forecast trial success and patient dropout rates.
Current treatment options and approved therapies vary widely depending on the therapeutic area. However, the process of matching patients to these treatments through clinical trials remains a critical bottleneck in drug development. Traditional methods of patient recruitment, such as physician referrals and media advertising, are being supplemented or replaced by more targeted, data-driven approaches enabled by matching software.
Upcoming therapies and technologies in the clinical trials matching space include:
- AI-powered natural language processing to extract relevant patient information from unstructured medical records.
- Blockchain technology for secure and transparent patient data sharing across institutions.
- Advanced predictive modeling to identify potential trial participants before they even seek treatment.
- Integration of wearable device data to expand the pool of real-world evidence for trial matching.
Breakthrough treatment options currently being developed often rely on highly specific patient characteristics, making efficient matching crucial. For instance, CAR-T cell therapies in oncology require precise genetic markers, and clinical trials matching software is evolving to incorporate these complex criteria.
The market composition is diverse, with a mix of established healthcare IT companies, specialized clinical research organizations (CROs), and innovative startups. While there are some dominant players, the market is not heavily consolidated, allowing for significant innovation and competition. The presence of both proprietary and open-source solutions contributes to a dynamic market environment.
Market Report Scope:
|
Key Insights |
Description |
|
The market size in 2024 |
US$ 1.85 Bn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
12.15% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 4.1 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2024 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
IBM Watson Health, Antidote Technologies Ltd., TrialSpark Inc., Unify Trials, Koneksa Health, TriNetX LLC, Match My Trial, Deep 6 AI, SubjectWell, Clinerion Ltd., Mendel.ai, Reify Health Inc., TrialX, Massive Bio, Veristat LLC |
Market Drivers:
Increasing complexity and volume of clinical trials
The growing complexity and sheer volume of clinical trials are driving significant demand for advanced clinical trials matching software. As the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries continue to expand their research and development efforts, the number of clinical trials being conducted globally has surged dramatically. This exponential growth has made it increasingly challenging for researchers and healthcare providers to efficiently match suitable patients with appropriate clinical trials using traditional methods.
Clinical trials matching software addresses this challenge by leveraging sophisticated algorithms and data analytics to streamline the patient recruitment process. These platforms can rapidly sift through vast amounts of patient data, including electronic health records, genetic information, and demographic details, to identify potential trial participants who meet specific eligibility criteria. This capability is particularly crucial for complex trials targeting rare diseases or highly specific patient populations.
For instance, in oncology research, where precision medicine approaches are becoming more prevalent, matching software can identify patients with specific genetic mutations or biomarkers that align with targeted therapies being tested in trials. This level of precision in patient matching not only accelerates the recruitment process but also enhances the overall quality and relevance of trial data collected, potentially leading to more successful outcomes and faster drug development timelines.
Emphasis on patient-centric approaches in clinical research
The shift towards patient-centric approaches in clinical research is a significant driver for the adoption of clinical trials matching software. As the healthcare industry increasingly recognizes the importance of patient engagement and experience in successful trial outcomes, there is a growing need for tools that can facilitate more personalized and accessible trial participation opportunities for patients.
Clinical trials matching software plays a crucial role in this patient-centric paradigm by empowering patients to take a more active role in their healthcare decisions. These platforms often feature user-friendly interfaces that allow patients to input their medical information and preferences, enabling them to explore potential trial opportunities that align with their specific conditions and circumstances. This level of patient involvement not only improves trial awareness and accessibility but also enhances patient satisfaction and retention rates throughout the study duration.
Moreover, advanced matching software can consider factors beyond mere clinical eligibility, such as a patient's location, lifestyle, and personal preferences, to suggest trials that are most likely to be feasible and appealing to individual participants. This holistic approach to trial matching can significantly reduce barriers to participation, such as travel distance or scheduling conflicts, which have traditionally hindered patient enrollment and retention in clinical studies.
By facilitating better-informed decision-making and more convenient trial options for patients, clinical trials matching software is helping to foster a more collaborative and patient-focused research environment. This alignment with patient-centric principles is driving increased adoption of these technologies across the clinical research landscape.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies are propelling the evolution and adoption of clinical trials matching software. These cutting-edge technologies are enhancing the capabilities of matching platforms, enabling them to process and analyze vast amounts of complex medical data with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
AI-powered clinical trials matching software can now interpret unstructured data from various sources, including medical literature, clinical notes, and imaging studies, to identify potential trial candidates who might have been overlooked by traditional screening methods. This ability to extract meaningful insights from diverse data types significantly expands the pool of potential participants and improves the precision of patient-trial matches.
Furthermore, machine learning algorithms continuously refine and improve their matching capabilities based on historical data and outcomes. As these systems process more information over time, they become increasingly adept at predicting which patients are most likely to benefit from specific trials and which trials are most likely to succeed with certain patient populations. This predictive capability not only enhances the efficiency of the recruitment process but also contributes to better overall trial design and execution.
The integration of natural language processing (NLP) in these platforms is another AI-driven advancement that is transforming the clinical trials matching landscape. NLP allows software to interpret and analyze free-text medical records and patient-reported outcomes, enabling a more nuanced understanding of patient eligibility and suitability for specific trials. This capability is particularly valuable in capturing subtle clinical details that might be missed in structured data fields alone.
Regulatory support for digital health technologies
The growing regulatory support for digital health technologies is serving as a significant driver for the clinical trials matching software market. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of digital solutions to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical research, leading to more favorable policies and guidelines for their implementation.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been proactive in embracing digital health technologies in clinical trials. The agency's Digital Health Innovation Action Plan and subsequent guidances have provided a clear regulatory framework for the development and use of digital tools in clinical research, including patient matching and recruitment technologies. This regulatory clarity has instilled confidence among both software developers and clinical trial sponsors, encouraging wider adoption of these innovative solutions.
Similarly, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has shown support for the use of digital technologies in clinical trials through various initiatives and guidances. The EMA's efforts to harmonize data standards and promote the use of electronic health records in clinical research have created a conducive environment for the implementation of advanced trial matching software across Europe.
These regulatory developments have not only legitimized the use of digital matching platforms but have also spurred innovation in the field. Software developers are now more confident in investing resources to create sophisticated, compliant solutions that meet the stringent requirements of clinical research. Additionally, the regulatory emphasis on data privacy and security has led to the development of robust, trustworthy platforms that can handle sensitive patient information in accordance with global data protection regulations.
Market Opportunities:
Integration with wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies
The integration of clinical trials matching software with wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies presents a significant opportunity for market expansion and innovation. As the healthcare industry increasingly embraces remote patient monitoring and decentralized clinical trials, there is a growing need for sophisticated software that can incorporate real-time patient data from wearable devices into the trial matching process.
This integration would allow for more dynamic and continuous patient screening, enabling researchers to identify potential trial participants based on up-to-date health metrics and behaviors. For instance, a smartwatch that tracks heart rate variability and sleep patterns could provide valuable data for matching patients to cardiovascular or sleep disorder trials. This real-time data capture could significantly enhance the precision of patient-trial matches and potentially identify eligible participants who might have been overlooked through traditional screening methods.
Moreover, the combination of wearable technology and matching software could facilitate the conduct of more flexible, patient-friendly trials. By enabling remote data collection and monitoring, this integrated approach could reduce the need for frequent in-person visits, making trial participation more accessible to a broader range of patients, including those in rural or underserved areas. This could lead to more diverse and representative patient populations in clinical studies, ultimately improving the generalizability of trial results.
The potential for this integration extends beyond just recruitment. Throughout the duration of a trial, continuous data from wearable devices could be used to monitor patient adherence, track outcomes, and even trigger alerts for potential adverse events. This level of real-time insight could dramatically improve trial efficiency and patient safety, opening up new possibilities for adaptive trial designs and personalized interventions.
Expansion into emerging markets and underserved populations
The expansion of clinical trials matching software into emerging markets and underserved populations represents a substantial opportunity for market growth and global health improvement. As clinical research increasingly seeks to diversify patient populations and address health disparities, there is a pressing need for tools that can facilitate trial access in regions traditionally underrepresented in medical studies.
In emerging markets, where healthcare infrastructure may be less developed, clinical trials matching software can play a crucial role in bridging the gap between patients and cutting-edge medical research. By leveraging mobile technologies and cloud-based platforms, these software solutions can reach patients in remote or resource-limited settings, connecting them with trial opportunities that were previously inaccessible. This expansion not only broadens the participant pool for global trials but also brings innovative treatments to populations that often lack access to advanced healthcare options.
Furthermore, adapting matching software to address the specific needs and challenges of underserved populations in developed countries presents another significant opportunity. This could involve creating culturally sensitive interfaces, supporting multiple languages, and incorporating social determinants of health into the matching algorithms. By doing so, the software can help address longstanding disparities in clinical trial participation among minority groups, elderly populations, and individuals with lower socioeconomic status.
The potential impact of this expansion goes beyond just increasing trial enrollment numbers. By facilitating more diverse and representative patient populations in clinical studies, these software solutions can contribute to the development of treatments that are more effective across different demographic groups. This approach aligns with the growing emphasis on precision medicine and could lead to more equitable health outcomes globally.
Development of therapeutic area-specific matching platforms
The development of therapeutic area-specific clinical trials matching platforms presents a significant opportunity for market expansion and specialization. As medical research becomes increasingly complex and targeted, there is a growing demand for matching software that can cater to the unique requirements of specific disease areas or treatment modalities.
Specialized matching platforms could offer more nuanced and precise patient-trial matching capabilities by incorporating deep domain knowledge of particular therapeutic areas. For instance, a platform dedicated to oncology trials could integrate detailed genomic profiling data, tumor characteristics, and treatment history to match patients with highly targeted experimental therapies. Similarly, a platform focused on rare diseases could incorporate specific biomarkers, genetic mutations, and symptom patterns that are crucial for identifying eligible patients in these often challenging-to-recruit studies.
These specialized platforms could also feature customized user interfaces and workflows tailored to the needs of both patients and researchers in specific therapeutic areas. For patients, this could mean more relevant and understandable trial information, while for researchers, it could provide more sophisticated screening tools and predictive analytics specific to their field of study.
Moreover, therapeutic area-specific platforms could facilitate closer collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patient advocacy groups within particular disease communities. By creating a focused ecosystem for specific conditions, these platforms could become valuable hubs for knowledge sharing, patient education, and community building, extending their value beyond mere trial matching.
Integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems
The integration of clinical trials matching software with electronic health records (EHR) systems represents a significant opportunity for enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of patient recruitment. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to digitize patient information, there is immense potential to leverage this vast repository of clinical data for more effective trial matching.
Seamless integration with EHR systems would allow clinical trials matching software to access comprehensive, up-to-date patient information in real-time. This integration could enable automatic pre-screening of patients based on their medical histories, current medications, lab results, and other clinical parameters. By doing so, it could dramatically reduce the time and resources typically required for manual chart reviews and initial eligibility assessments.
Furthermore, EHR integration could facilitate proactive trial matching, where the software continuously scans patient records to identify potential candidates as soon as they become eligible for a study. This approach could significantly reduce delays in patient recruitment and help to identify suitable participants who might otherwise be overlooked in busy clinical settings.
The potential benefits extend to patient care as well. Integration with EHR systems could allow for better coordination between clinical research and routine patient care. Healthcare providers could be automatically notified of potentially relevant trials for their patients, enabling them to discuss these opportunities as part of regular care consultations. This seamless flow of information could help to normalize clinical trial participation as a standard care option, potentially increasing overall trial awareness and enrollment rates.
Market Trends:
Rise of decentralized and virtual clinical trials
The increasing adoption of decentralized and virtual clinical trials is a significant trend shaping the clinical trials matching software market. As the pharmaceutical industry seeks to make trials more patient-centric and resilient to disruptions, there's a growing shift towards trial designs that minimize the need for in-person site visits and allow for remote patient participation.
This trend has been accelerated by recent global events, which have highlighted the vulnerabilities of traditional site-based trial models. In response, sponsors and contract research organizations are rapidly embracing technologies that enable remote patient screening, enrollment, and monitoring. Clinical trials matching software is evolving to support these decentralized models by incorporating features that assess a patient's suitability for remote participation based on factors such as their technological capabilities, home environment, and ability to self-administer treatments.
Moreover, these platforms are increasingly integrating with telemedicine tools, electronic consent systems, and home health services to create comprehensive ecosystems for virtual trial conduct. This integration allows for a seamless patient journey from initial matching to trial completion, all managed through digital interfaces. The software is also being adapted to support hybrid trial models, where patients may participate in a mix of in-person and virtual study activities.
As decentralized trials continue to gain traction, clinical trials matching software is likely to play an even more crucial role in identifying and engaging suitable participants across wider geographical areas, potentially leading to more diverse and representative study populations.
Emphasis on real-world evidence and pragmatic trials
The growing emphasis on real-world evidence (RWE) and pragmatic clinical trials is emerging as a significant trend influencing the clinical trials matching software market. Regulatory bodies and healthcare payers are increasingly recognizing the value of evidence generated from real-world settings to complement traditional randomized controlled trials.
This shift is driving the development of clinical trials matching software that can identify and recruit patients from diverse real-world settings, including primary care clinics, community hospitals, and specialty practices. These platforms are being enhanced to consider a broader range of patient characteristics and environmental factors that are relevant to pragmatic trial designs, such as comorbidities, concomitant medications, and socioeconomic factors.
Furthermore, matching software is evolving to support the design and execution of large-scale pragmatic trials by leveraging diverse data sources, including electronic health records, claims databases, and patient registries. This capability allows researchers to identify eligible patient populations that are more representative of real-world clinical practice, potentially leading to more generalizable and clinically relevant results.
The trend towards RWE is also influencing the development of post-marketing surveillance features within clinical trials matching software. These tools can help identify patients for long-term follow-up studies or observational research, enabling the continuous collection of real-world data on treatment effectiveness and safety long after a product has been approved.
Incorporation of patient-reported outcomes and preferences
The increasing focus on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and patient preferences in clinical research is a notable trend affecting the clinical trials matching software market. As the healthcare industry moves towards more patient-centric approaches, there's a growing recognition of the importance of incorporating patients' perspectives and experiences into trial design and execution.
Clinical trials matching software is adapting to this trend by integrating features that capture and analyze patient-reported data as part of the matching process. These platforms are being enhanced to collect information on patients' quality of life, symptom burden, and treatment preferences, in addition to traditional clinical eligibility criteria. This holistic approach to patient matching not only improves the relevance of trial recommendations for individual patients but also contributes to better overall trial design and patient retention.
Moreover, matching software is increasingly incorporating tools for ongoing collection and analysis of PROs throughout the duration of a trial. This capability allows for real-time monitoring of patient experiences and outcomes, potentially enabling more adaptive and responsive trial management. It also aligns with the growing interest in patient-centric endpoints and their inclusion in regulatory decision-making.
The trend towards greater inclusion of patient voices is also reflected in the development of more engaging and interactive user interfaces within matching software. These interfaces are being designed to facilitate better communication of trial information to patients, helping them make more informed decisions about participation based on their personal goals and preferences.
Application of predictive analytics and machine learning
The application of predictive analytics and machine learning in clinical trials matching software is an emerging trend that is transforming the landscape of patient recruitment and trial optimization. As the volume and complexity of clinical data continue to grow, there's an increasing need for sophisticated analytical tools that can extract meaningful insights and predict outcomes.
Clinical trials matching software is increasingly incorporating advanced predictive models that can forecast a patient's likelihood of meeting all inclusion/exclusion criteria, adhering to the study protocol, and potentially benefiting from the experimental treatment. These predictive capabilities are enhancing the precision of patient-trial matches, potentially leading to higher enrollment rates, reduced screen failures, and improved trial retention.
Moreover, machine learning algorithms are being applied to continuously refine and improve matching algorithms based on historical trial data and outcomes. These self-learning systems can identify patterns and correlations that might not be apparent through traditional statistical methods, potentially uncovering new insights into factors that contribute to successful trial participation and outcomes.
The trend towards predictive analytics is also extending beyond patient matching to encompass broader aspects of trial planning and management. Advanced matching platforms are beginning to offer features that can predict site performance, estimate recruitment timelines, and even suggest optimal protocol designs based on analysis of past trial data and current patient populations.
Market Restraints:
Data privacy and security concerns
Data privacy and security concerns pose a significant restraint to the widespread adoption and implementation of clinical trials matching software. As these platforms handle sensitive patient health information and proprietary trial data, there are substantial risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and potential misuse of information.
The healthcare industry is subject to stringent data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Compliance with these regulations can be complex and costly for software developers, potentially limiting innovation and market entry for smaller players. Moreover, the global nature of many clinical trials introduces additional challenges in navigating varying international data protection laws and ensuring cross-border data transfers are compliant and secure.
Patient trust is another critical factor affected by data privacy concerns. Individuals may be hesitant to share their personal health information with matching platforms due to fears about how their data might be used or shared. This reluctance can significantly impact the effectiveness of matching software, as the quality and completeness of patient data are crucial for accurate matching.
High Implementation Costs
The high implementation costs associated with Clinical Trials Matching Software present a significant barrier to market growth, especially for smaller organizations and research institutions. Deploying these sophisticated software solutions often requires substantial upfront investments in technology infrastructure, data integration, and staff training. The complexity of these systems may necessitate extensive customization to align with existing workflows and IT ecosystems, further driving up costs.
Additionally, ongoing maintenance, updates, and technical support contribute to the total cost of ownership. For many organizations, particularly those with limited budgets or those in developing countries, these financial barriers can be prohibitive. The perceived ROI may not be immediately apparent, making it challenging to justify the expenditure, especially for institutions that conduct fewer clinical trials or have smaller patient populations. This cost factor can slow down the adoption rate of clinical trial matching software, limiting market expansion.
Lack of Standardization in Clinical Trial Processes
The lack of standardization in clinical trial processes across different organizations and regions poses a significant challenge to the widespread adoption of Clinical Trials Matching Software. Clinical trials vary considerably in their design, data collection methods, and reporting standards, making it difficult to create a one-size-fits-all software solution. This variability can lead to challenges in data integration, interoperability, and the ability to conduct cross-trial analyses effectively.
Furthermore, the absence of universally accepted standards for patient matching criteria and trial eligibility can result in inconsistencies in how different software platforms interpret and apply these criteria. This lack of standardization can lead to discrepancies in patient matching results across different systems, potentially undermining confidence in the technology. It also complicates the process of validating and comparing the effectiveness of various clinical trial matching software solutions, making it harder for potential adopters to make informed decisions about which platform to choose.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Company Name |
|
In March 2023, TriNetX launched TriNetX Connect, a new platform that enables clinical research teams to collaborate seamlessly across the entire trial lifecycle. This development enhances the efficiency of trial design, site selection, and patient recruitment processes. |
TriNetX |
|
Medidata, a Dassault Systèmes company, introduced its Medidata Link solution in June 2022. This tool uses AI to connect clinical trial data with real-world data, improving patient matching and long-term outcome tracking for trials. |
Medidata Solutions (Dassault Systèmes) |
|
IQVIA unveiled its Avacare Clinical Research Network in September 2022, integrating clinical research into everyday care settings. This network aims to expand patient access to clinical trials and streamline the matching process. |
IQVIA |
|
In April 2022, Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner, a major electronic health records provider. This merger has significant implications for clinical trials matching, potentially integrating trial recruitment directly into health IT systems. |
Oracle Corporation |
|
IBM Watson Health launched IBM Study Advance in September 2020, an AI-powered solution designed to optimize clinical trial protocol design and potentially improve patient matching processes. |
IBM Watson Health |
|
Antidote Technologies released Antidote Match 2.0 in May 2021, featuring enhanced machine learning capabilities for more precise patient-trial matching and improved user experience for patients seeking trials. |
Antidote Technologies |
|
In January 2022, Reify Health acquired StudyTeam, expanding its capabilities in clinical trial recruitment and site selection. This acquisition aims to accelerate clinical research by improving the efficiency of patient enrollment. |
Reify Health |
|
TrialSpark announced a $156 million Series C funding round in October 2021, supporting the expansion of its tech-enabled clinical trial platform that includes advanced patient matching capabilities. |
TrialSpark |
|
Deep 6 AI partnered with Cerner in March 2021 to integrate its AI-powered clinical trials acceleration software with Cerner's electronic health record systems, enhancing patient identification for trials. |
Deep 6 AI |
|
SubjectWell launched its Marketplace solution in February 2022, creating a centralized platform for matching patients with multiple clinical trial opportunities across various sponsors and research sites. |
SubjectWell |
Market Regional Insights:
The global Clinical Trials Matching Software Market exhibits varying growth patterns across different regions, influenced by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, R&D investment, regulatory environments, and technological adoption rates. North America currently leads the market, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific. The market in emerging economies is showing promising growth potential, driven by increasing clinical trial activities and improving healthcare IT infrastructure.
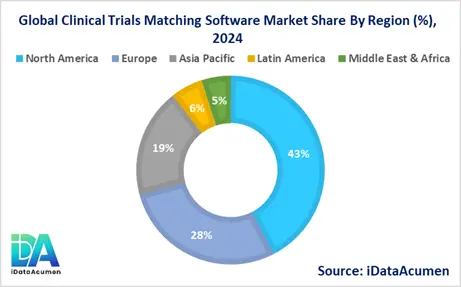
- North America is expected to be the largest market for Clinical Trials Matching Software during the forecast period, accounting for over 42.5% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the presence of major pharmaceutical companies, high R&D expenditure, and advanced healthcare IT infrastructure. The region's strong focus on precision medicine and patient-centric healthcare also drives the adoption of sophisticated matching technologies.
- The European market is expected to be the second-largest market for Clinical Trials Matching Software, accounting for over 28.3% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market is attributed to stringent regulatory requirements for clinical trials, increasing collaboration between academia and industry, and growing government initiatives to promote clinical research.
- The Asia Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Clinical Trials Matching Software, with a CAGR of over 14.5% during the forecast period by 2024. The growth of the market in Asia Pacific is attributed to the rising number of clinical trials in countries like China and India, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing investment in healthcare IT solutions. This region also holds the third-largest share at 18.7% of the global market.
Market Segmentation:
- By Deployment Model
- Cloud-based
- On-premises
- Hybrid
- By End User
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Academic and research institutions
- Healthcare providers
- Government organizations
- Patient advocacy groups
- Others (e.g., biotechnology companies, medical device manufacturers)
- By Functionality
- Patient recruitment and screening
- Protocol feasibility analysis
- Site selection and management
- Patient retention and engagement
- Data analytics and reporting
- Regulatory compliance management
- Others (e.g., budget management, document management)
- By Clinical Trial Phase
- Phase I
- Phase II
- Phase III
- Phase IV
- Others (e.g., observational studies, registries)
- By Therapeutic Area
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Infectious diseases
- Neurology
- Immunology
- Rare diseases
- Others (e.g., dermatology, endocrinology, respiratory diseases)
- By Organization Size
-
- Large enterprises
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
-
- By Component
- Software
- Services
- Professional services
- Managed services
- Hardware
- By Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Market Segmental Analysis:
- By Deployment Model: The cloud-based segment is expected to experience the highest growth, with a projected CAGR of 14.2% from 2024 to 2031. This growth is particularly strong in North America and Europe due to the increasing adoption of cloud technologies in healthcare. The cloud-based segment is estimated to be the largest in 2024, accounting for approximately 55% of the market share.
- By End User: Pharmaceutical companies are projected to remain the largest segment in 2024, holding about 40% of the market share. However, the Contract Research Organizations (CROs) segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate, with a CAGR of 13.5% during the forecast period. This growth is particularly notable in the Asia Pacific region, where many global pharmaceutical companies are outsourcing clinical trials.
- By Therapeutic Area: The oncology segment is anticipated to be both the largest and fastest-growing segment, with a market share of around 30% in 2024 and a CAGR of 13.8% through 2031. This growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of cancer worldwide and the rising number of oncology clinical trials, especially in North America and Europe.
These projections highlight the dynamic nature of the Clinical Trials Matching Software Market, with cloud-based solutions, CROs, and oncology-focused applications leading the growth across various segments and regions.
Top Companies in the Clinical Trials Matching Software Market:
- IBM Watson Health
- Oracle Corporation
- Medidata Solutions (Dassault Systèmes)
- IQVIA
- TriNetX
- Accenture
- Cognizant
- Parexel International Corporation
- TrialSpark
- Deep 6 AI
- Antidote Technologies
- Inspirata
- SubjectWell
- Reify Health
- Clinerion
- TrialWire
- Elligo Health Research
- Koneksa Health
- Clinical Research IO
- TransMed Systems