Market Analysis:
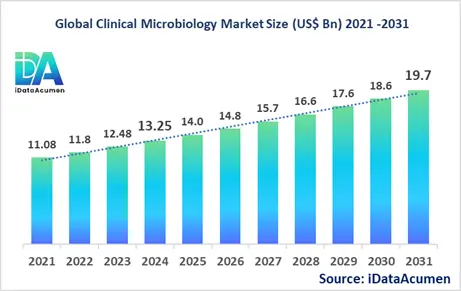
The Clinical Microbiology Market had an estimated market size worth US$ 13.25 billion in 2024, and it is predicted to reach a global market valuation of US$ 19.7 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2031.
Clinical microbiology is a critical branch of medical science that focuses on the identification, diagnosis, and treatment of infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. This field employs various techniques and technologies to detect, isolate, and characterize pathogens in clinical specimens, including blood, urine, tissue samples, and other bodily fluids. The primary goal of clinical microbiology is to provide accurate and timely information to healthcare providers, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care and treatment strategies.
The advantages of clinical microbiology are numerous and significant. Firstly, it allows for precise identification of disease-causing organisms, which is crucial for selecting appropriate antimicrobial therapies. This targeted approach helps reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, thereby mitigating the risk of antimicrobial resistance. Secondly, clinical microbiology plays a vital role in infection control and prevention within healthcare settings by identifying outbreaks and guiding containment measures. Additionally, it contributes to public health surveillance, helping to track and monitor the spread of infectious diseases on a larger scale.
The growth of the Clinical Microbiology Market is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of infectious diseases globally, the rising threat of antimicrobial resistance, and the growing demand for rapid and accurate diagnostic tools. Technological advancements in molecular diagnostics and automation have also significantly contributed to market expansion.
The Clinical Microbiology Market is segmented by product type, application, technology, end-user, test type, disease area, specimen type, and region. By product type, the market is segmented into instruments, reagents, consumables, and software & services. The reagents segment is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for ready-to-use, standardized diagnostic kits and the continuous need for these products in routine clinical testing.
A notable example of recent technological advancement in this segment is the introduction of the BD MAX™ System by Becton, Dickinson and Company. This fully automated molecular diagnostics platform enables laboratories to perform a wide range of molecular tests with minimal hands-on time, improving efficiency and accuracy in clinical microbiology testing.
Epidemiology Insights:
The burden of infectious diseases varies significantly across major regions, with developing countries generally facing a higher incidence of communicable diseases compared to developed nations. In North America and Europe, healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and antibiotic-resistant pathogens pose significant challenges. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that about 1 in 31 hospital patients has at least one HAI on any given day in the United States.
Key epidemiological trends in major markets such as the US, EU5 (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK), and Japan include the rising prevalence of antibiotic-resistant infections, an aging population more susceptible to infections, and the emergence of new pathogens. The COVID-19 pandemic has also significantly impacted the epidemiological landscape, highlighting the importance of robust clinical microbiology capabilities.
Recent data indicates that the incidence of certain infectious diseases is on the rise in major markets. For instance, the CDC reports that cases of certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) have reached record highs in the United States, with over 2.5 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported in 2019. In Europe, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) has noted an increase in Legionnaires' disease cases, with a 58% rise between 2015 and 2019.
The changing epidemiological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for the Clinical Microbiology Market. The increasing patient population for various infectious diseases drives demand for diagnostic tests and treatment options. However, it also underscores the need for more advanced, rapid, and accurate diagnostic tools to manage the growing disease burden effectively.
While many infectious diseases addressed by clinical microbiology are common, the field also plays a crucial role in identifying and managing rare diseases. For example, certain fungal infections or tropical diseases may be considered rare in some regions but require specialized diagnostic capabilities. The ability to diagnose these rare conditions accurately is essential for proper patient management and epidemiological tracking.
Market Landscape:
Despite significant advancements in clinical microbiology, several unmet needs persist in the market. One of the primary challenges is the need for faster and more accurate diagnostic methods, particularly for antibiotic-resistant pathogens. There is also a growing demand for point-of-care testing solutions that can provide rapid results in various healthcare settings, including remote or resource-limited areas.
Current treatment options in clinical microbiology primarily revolve around antimicrobial therapies. Approved therapies include a wide range of antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, and antiparasitic drugs. For example, broad-spectrum antibiotics like amoxicillin-clavulanate and ciprofloxacin are commonly used for bacterial infections, while fluconazole and voriconazole are standard treatments for fungal infections.
Upcoming therapies and technologies in the clinical microbiology market are focusing on addressing the challenges of antimicrobial resistance and improving diagnostic accuracy. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies are being developed for rapid pathogen identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Companies are also investing in AI-powered diagnostic platforms that can analyze complex microbial data and provide more accurate results.
Breakthrough treatment options currently under development include novel antimicrobial agents targeting multidrug-resistant pathogens. For instance, researchers are exploring antimicrobial peptides, phage therapy, and CRISPR-based antimicrobials as potential alternatives to traditional antibiotics. Additionally, there is growing interest in microbiome-based therapies, which aim to restore balance to the body's microbial communities rather than simply eliminating pathogens.
The Clinical Microbiology Market comprises both generic and branded product manufacturers. While generic manufacturers play a significant role in providing cost-effective diagnostic reagents and antimicrobial drugs, the market also sees substantial participation from branded manufacturers, particularly in the development of advanced diagnostic instruments and novel therapeutic approaches. The increasing complexity of infectious diseases and the need for specialized diagnostic tools have created opportunities for niche players to enter the market with innovative solutions.
Market Report Scope:
|
Key Insights |
Description |
|
The market size in 2024 |
US$ 13.25 Bn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
5.8% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 19.7 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2024 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Abbott Laboratories, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Becton, Dickinson and Company, bioMérieux SA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Bruker Corporation, Danaher Corporation, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Hologic, Inc., Merck KGaA, QIAGEN N.V., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. |
Market Drivers:
Rising Prevalence of Infectious Diseases
The increasing prevalence of infectious diseases worldwide is a significant driver propelling the growth of the clinical microbiology market. As populations grow and become more interconnected through globalization and travel, the spread of infectious pathogens has accelerated. This trend has created an urgent need for advanced clinical microbiology techniques to rapidly identify and characterize disease-causing microorganisms.
Recent outbreaks of novel pathogens have further highlighted the critical role of clinical microbiology. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the importance of robust testing capabilities and microbial surveillance systems. Health organizations worldwide have since prioritized strengthening their clinical microbiology infrastructure to better respond to future outbreaks.
Additionally, the rise of antimicrobial resistance has intensified the demand for sophisticated microbiology testing. As traditional antibiotics lose effectiveness against evolving pathogens, there is a growing need for rapid diagnostic tools to guide targeted therapies. This has spurred innovation in areas such as molecular diagnostics and automated identification systems within the clinical microbiology field.
Furthermore, emerging infectious diseases in previously unaffected regions, often linked to climate change and ecological disruptions, have expanded the scope of clinical microbiology applications. This has led to increased investments in research and development of new diagnostic technologies tailored to detect and monitor these novel threats.
Technological Advancements in Diagnostic Techniques
Rapid technological advancements in diagnostic techniques are revolutionizing the field of clinical microbiology and driving market growth. These innovations are enhancing the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of microbial identification and characterization, enabling healthcare providers to make more informed treatment decisions.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have emerged as a game-changer in clinical microbiology. NGS allows for comprehensive genomic analysis of pathogens, providing detailed information about virulence factors, antibiotic resistance genes, and phylogenetic relationships. This level of insight is invaluable for outbreak investigations and personalized treatment approaches.
Mass spectrometry, particularly MALDI-TOF (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight), has gained widespread adoption in clinical laboratories. This technology enables rapid and accurate identification of microorganisms based on their unique protein profiles, significantly reducing the time required for diagnosis compared to traditional culture-based methods.
Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming workflow efficiency in clinical microbiology laboratories. Advanced laboratory information systems and robotic platforms are streamlining sample processing, data analysis, and result reporting. Machine learning algorithms are being developed to assist in interpreting complex microbiology data, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and consistency.
Point-of-care testing devices for infectious diseases are also advancing rapidly. These portable, user-friendly systems bring sophisticated molecular diagnostic capabilities closer to patients, enabling faster treatment decisions in various healthcare settings, from hospitals to remote clinics.
Growing Emphasis on Early Disease Detection and Prevention
The increasing focus on early disease detection and prevention strategies is a key driver for the clinical microbiology market. Healthcare systems worldwide are recognizing the clinical and economic benefits of identifying and addressing infectious diseases in their early stages, leading to greater investments in advanced microbiology diagnostics.
Preventive healthcare programs are expanding their scope to include more comprehensive microbial screening. For example, many countries have implemented broader screening protocols for healthcare-associated infections, sexually transmitted diseases, and foodborne pathogens. These initiatives require sophisticated clinical microbiology tools to process large numbers of samples efficiently and accurately.
The concept of antimicrobial stewardship has gained significant traction in recent years. Healthcare facilities are implementing programs to optimize antibiotic use, which rely heavily on rapid and precise microbial identification and susceptibility testing. This trend has boosted demand for advanced clinical microbiology systems that can provide timely, actionable results to guide appropriate antibiotic prescribing.
Public health surveillance efforts have also intensified, particularly in the wake of recent epidemics. Governments and health organizations are investing in robust microbiology infrastructure to monitor and track potential outbreaks. This includes the establishment of reference laboratories equipped with cutting-edge diagnostic technologies and the implementation of digital surveillance systems that rely on real-time microbiology data.
The growing awareness of the microbiome's role in human health has opened new avenues for clinical microbiology applications. Research into the complex interactions between microbial communities and human health is driving the development of novel diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies, further expanding the scope of the clinical microbiology market.
Increasing Healthcare Expenditure and Infrastructure Development
Rising healthcare expenditure and ongoing infrastructure development in both developed and emerging economies are significant drivers for the clinical microbiology market. As countries invest more in their healthcare systems, there is a corresponding increase in the adoption of advanced medical technologies, including state-of-the-art clinical microbiology equipment and techniques.
In developed nations, the modernization of existing healthcare facilities often includes upgrades to clinical laboratories. Hospitals and diagnostic centers are investing in automated microbiology systems, molecular diagnostic platforms, and advanced information management solutions to enhance their testing capabilities and operational efficiency.
Emerging economies are experiencing rapid growth in healthcare infrastructure, with the construction of new hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic laboratories. This expansion is creating fresh demand for clinical microbiology products and services. Governments in these countries are also increasing their healthcare budgets, allocating funds for the acquisition of modern diagnostic technologies to improve disease management and public health outcomes.
The private healthcare sector is playing an increasingly important role in driving market growth. Private hospital chains and diagnostic laboratory networks are expanding their presence, often equipped with the latest clinical microbiology technologies to gain a competitive edge. This trend is particularly notable in countries with growing middle-class populations seeking high-quality healthcare services.
Global health initiatives and international aid programs are also contributing to the development of clinical microbiology capabilities in resource-limited settings. These programs often include provisions for establishing or upgrading microbiology laboratories, creating new market opportunities for diagnostic equipment and reagent suppliers.
Market Opportunities:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into clinical microbiology presents a significant opportunity for market growth and innovation. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize various aspects of microbial diagnostics, from sample analysis to result interpretation and clinical decision support.
AI algorithms can enhance the accuracy and speed of microbial identification by analyzing complex data from various diagnostic modalities. For instance, machine learning models can be trained to recognize subtle patterns in microscopy images, mass spectrometry data, or genetic sequences that might be challenging for human experts to discern consistently. This could lead to more precise and rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases.
In the realm of antimicrobial susceptibility testing, AI-driven systems could predict resistance patterns based on genomic data, potentially bypassing time-consuming phenotypic testing methods. This approach could dramatically reduce the time required to determine effective treatment options, especially for critically ill patients with drug-resistant infections.
The application of AI in clinical microbiology extends to epidemiological surveillance and outbreak prediction. By analyzing vast amounts of microbiology data in real-time, AI systems could identify emerging patterns and alert public health authorities to potential outbreaks before they become widespread. This proactive approach could significantly improve infectious disease control and prevention strategies.
Development of Multiplex and Syndromic Testing Platforms
The development and expansion of multiplex and syndromic testing platforms represent a promising opportunity in the clinical microbiology market. These advanced diagnostic tools allow for the simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens or genetic markers from a single patient sample, offering a more comprehensive and efficient approach to infectious disease diagnosis.
Syndromic testing panels are particularly valuable in scenarios where patients present with similar symptoms that could be caused by various pathogens. For example, respiratory or gastrointestinal infection panels can quickly identify the causative agent among a range of possible viral, bacterial, or fungal pathogens. This approach not only speeds up diagnosis but also helps in avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, supporting antimicrobial stewardship efforts.
The convenience and rapid turnaround time of multiplex testing make it increasingly attractive for point-of-care applications. There is growing interest in developing portable, easy-to-use multiplex platforms that can be deployed in various healthcare settings, from emergency rooms to remote clinics. This trend could significantly expand the reach of advanced clinical microbiology diagnostics.
As new pathogens emerge and our understanding of microbial interactions deepens, there is an opportunity to develop increasingly sophisticated and comprehensive testing panels. Future multiplex assays might incorporate markers for antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors, or host response indicators, providing a more nuanced picture of the infection and guiding personalized treatment strategies.
Expansion of Microbiology Services in Personalized Medicine
The growing field of personalized medicine presents a significant opportunity for the clinical microbiology market to expand its role and services. As healthcare moves towards more individualized treatment approaches, there is increasing recognition of the importance of a patient's microbial profile in health and disease management.
Microbiome analysis is emerging as a key component of personalized healthcare. Clinical microbiology laboratories have the opportunity to develop and offer comprehensive microbiome profiling services, which could inform treatment decisions for a wide range of conditions, from gastrointestinal disorders to immunological diseases. This expansion into microbiome diagnostics requires the integration of advanced sequencing technologies and bioinformatics capabilities.
Personalized approaches to infectious disease management also offer growth opportunities. By combining pathogen identification with host genetic and immune response data, clinical microbiology services could provide more tailored treatment recommendations. This might include predicting an individual's susceptibility to certain infections or their likelihood of responding to specific antimicrobial therapies.
The concept of personalized vaccination strategies based on an individual's microbial and immunological profile is gaining traction. Clinical microbiology laboratories could play a crucial role in assessing a person's existing immunity and microbial exposures to guide vaccine recommendations. This personalized approach to preventive care could significantly enhance vaccine efficacy and public health outcomes.
Expansion into Environmental and Industrial Microbiology
The expertise and technologies developed in clinical microbiology have significant potential for application in environmental and industrial settings, presenting an opportunity for market expansion. As awareness of the impact of microbial communities on various ecosystems and industrial processes grows, there is increasing demand for advanced microbial analysis services.
Environmental microbiology applications offer a promising avenue for growth. Clinical microbiology techniques can be adapted to monitor water quality, assess soil health, or track microbial populations in various ecosystems. This is particularly relevant in the context of climate change and environmental conservation efforts, where understanding microbial dynamics is crucial for predicting and mitigating ecological changes.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant opportunity for clinical microbiology expansion. Advanced rapid testing methods developed for clinical diagnostics can be applied to food safety testing, helping to prevent foodborne illness outbreaks and ensure product quality. There is growing demand for sophisticated microbial analysis in food production, from raw material testing to final product verification.
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, clinical microbiology expertise is valuable for ensuring the safety and quality of products. This includes sterility testing of drugs and medical devices, monitoring of bioprocessing environments, and characterization of microbial strains used in bioproduction. As these industries continue to grow and face stricter regulatory requirements, the demand for specialized microbiology services is likely to increase.
Market Trends:
Shift Towards Molecular Diagnostics
A significant trend in the clinical microbiology market is the increasing shift towards molecular diagnostic methods. Traditional culture-based techniques, while still important, are being complemented or replaced by nucleic acid-based tests that offer faster and more precise results.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technologies have become a mainstay in many clinical microbiology laboratories. Real-time PCR assays are widely used for the rapid detection of pathogens, offering results in hours rather than days. The development of multiplex PCR panels has further enhanced the efficiency of diagnostic processes, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens in a single test.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is gaining traction in clinical microbiology applications. Whole genome sequencing of pathogens is becoming more accessible, providing unprecedented insights into microbial genetics, evolution, and antimicrobial resistance. This technology is particularly valuable for outbreak investigations and epidemiological studies.
Isothermal amplification techniques, such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), are emerging as alternatives to PCR in certain applications. These methods offer the advantage of rapid amplification at a constant temperature, making them suitable for point-of-care testing in resource-limited settings.
Automation and Integration of Laboratory Processes
The trend towards automation and integration of laboratory processes is reshaping the clinical microbiology landscape. Laboratories are increasingly adopting automated systems to improve efficiency, reduce human error, and handle growing test volumes.
Total laboratory automation (TLA) systems are being implemented in large clinical microbiology laboratories. These systems automate various steps of the microbiology workflow, from sample processing and inoculation to incubation and imaging of culture plates. This level of automation significantly reduces hands-on time and improves standardization of procedures.
Integration of different diagnostic platforms is another key aspect of this trend. Laboratory information systems (LIS) are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for seamless data flow between various instruments and departments. This integration enhances result reporting, improves traceability, and facilitates better clinical decision-making.
Artificial intelligence is being incorporated into automated systems to assist in data interpretation. Machine learning algorithms are being developed to analyze growth patterns on culture plates, interpret antibiotic susceptibility tests, and flag unusual results for review by microbiologists.
Rise of Point-of-Care Testing in Microbiology
Point-of-care testing (POCT) is gaining prominence in clinical microbiology, driven by the need for rapid diagnostic results in various healthcare settings. This trend is shifting some testing away from centralized laboratories to near-patient locations.
Molecular POCT devices for infectious diseases are becoming more widespread. These systems offer rapid detection of pathogens such as influenza, strep throat, or COVID-19 in clinics, emergency departments, and even community pharmacies. The ease of use and quick turnaround time of these tests allow for immediate treatment decisions.
Advances in microfluidics and biosensor technologies are enabling the development of more sophisticated POCT devices. These innovations are making it possible to perform complex microbiology tests, including antimicrobial susceptibility testing, in compact, user-friendly formats suitable for use outside of traditional laboratory settings.
The integration of POCT results with electronic health records and broader health information systems is an emerging focus. This connectivity ensures that point-of-care microbiology results are readily available to healthcare providers and can be integrated into overall patient management strategies.
Growing Focus on Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance
The global challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is driving a trend towards enhanced surveillance and monitoring in clinical microbiology. There is increasing emphasis on tracking resistance patterns and implementing strategies to preserve the effectiveness of existing antimicrobials.
Advanced diagnostic technologies are being deployed to rapidly detect and characterize resistant organisms. Molecular methods, including PCR and sequencing-based approaches, are being used to identify resistance genes and mechanisms, providing more comprehensive resistance profiles than traditional phenotypic methods alone.
Global and national AMR surveillance networks are being strengthened, with clinical microbiology laboratories playing a crucial role in data collection and reporting. These networks aim to provide real-time information on resistance trends, guiding public health interventions and informing antibiotic stewardship programs.
There is growing interest in using big data analytics and artificial intelligence to predict the emergence and spread of resistant pathogens. By analyzing large datasets from clinical microbiology laboratories, researchers hope to develop early warning systems for AMR threats and optimize treatment strategies.
Market Restraints:
High Costs Associated with Advanced Microbiology Systems
The high costs associated with advanced clinical microbiology systems and technologies pose a significant restraint to market growth. While these sophisticated tools offer improved efficiency and accuracy, their substantial initial investment and ongoing operational expenses can be prohibitive for many healthcare facilities, particularly in resource-limited settings.
State-of-the-art automated microbiology systems, molecular diagnostic platforms, and mass spectrometry instruments often come with hefty price tags. The cost of acquisition, installation, and staff training can strain budgets, especially for smaller laboratories or hospitals. This financial barrier can lead to slower adoption rates of new technologies, potentially creating disparities in diagnostic capabilities between well-funded and under-resourced healthcare facilities.
Ongoing expenses, including maintenance contracts, software updates, and specialized reagents, contribute to the total cost of ownership. These recurring costs can be challenging to sustain, particularly in healthcare systems facing budget constraints. As a result, some facilities may opt to continue using traditional, less expensive methods, even if they are less efficient or accurate.
The need for specialized personnel to operate and maintain advanced microbiology systems adds another layer of cost. Highly trained technicians and microbiologists command higher salaries, and ongoing professional development is necessary to keep pace with rapidly evolving technologies. This requirement for specialized human resources can be particularly challenging in regions facing healthcare workforce shortages.
Regulatory Challenges and Quality Control Issues
Regulatory challenges and quality control issues present significant restraints to the clinical microbiology market. The stringent regulatory environment surrounding diagnostic tests and laboratory practices, while necessary for ensuring patient safety and result accuracy, can slow down innovation and market entry for new technologies.
The process of obtaining regulatory approvals for new diagnostic tests and instruments is often lengthy and complex. This can delay the introduction of innovative technologies to the market, potentially hindering advancements in clinical microbiology. Smaller companies and startups may find it particularly challenging to navigate these regulatory hurdles, potentially stifling innovation in the field.
Stringent Regulatory Requirements
The clinical microbiology market faces significant challenges due to stringent regulatory requirements imposed by various health authorities worldwide. These regulations, while necessary to ensure patient safety and product efficacy, can often slow down the process of bringing new diagnostic tools and technologies to market. The lengthy and complex approval processes for new products can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially deterring smaller companies from entering the market or delaying the introduction of innovative solutions.
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe require extensive clinical trials and validation studies before approving new diagnostic tests or instruments. These requirements can lead to prolonged development cycles and increased costs for manufacturers. Additionally, the need to comply with different regulatory standards across various countries can further complicate market entry and expansion strategies for global companies.
The stringent regulations also extend to laboratory operations, requiring adherence to strict quality control measures and documentation procedures. This can increase operational costs and complexity for healthcare facilities, potentially limiting their ability to adopt new technologies or expand their microbiology services. As a result, the market may experience slower growth rates and reduced innovation, as companies navigate the complex regulatory landscape.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Company Name |
|
In March 2023, BioMérieux launched the VITEK® MS PRIME, a new MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry system for microbial identification. This system offers faster time-to-results and an expanded database, improving the efficiency of clinical microbiology laboratories. |
BioMérieux SA |
|
Roche introduced the cobas® 5800 System in January 2022, a compact molecular diagnostics system for detecting various pathogens. This launch expanded Roche's molecular testing portfolio, providing smaller and medium-sized laboratories with access to advanced PCR technology. |
Roche Diagnostics |
|
In September 2022, Thermo Fisher Scientific unveiled the Applied Biosystems™ QuantStudio™ 7 Pro Dx Real-Time PCR System for clinical diagnostics. This system offers improved sensitivity and flexibility for detecting a wide range of pathogens, enhancing laboratory capabilities. |
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. |
|
Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD) launched the BD COR™ PX/GX System in February 2021, an automated high-throughput diagnostic system for infectious diseases. This system significantly increases testing capacity and reduces hands-on time for laboratory staff. |
Becton, Dickinson and Company |
|
In July 2022, QIAGEN introduced the QIAstat-Dx Rise, an advanced syndromic testing system for simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens. This launch strengthened QIAGEN's position in the rapidly growing syndromic testing market. |
QIAGEN N.V. |
|
Bruker Corporation released the MALDI Biotyper® sirius system in April 2021, featuring new technologies for microbial identification and characterization. This system enhances the speed and accuracy of pathogen identification in clinical microbiology laboratories. |
Bruker Corporation |
|
In December 2022, Hologic acquired Mobidiag Oy for $795 million, expanding its molecular diagnostics portfolio. This acquisition strengthened Hologic's position in the acute care market and enhanced its infectious disease testing capabilities. |
Hologic, Inc. and Mobidiag Oy |
|
Danaher Corporation completed the acquisition of Aldevron for $9.6 billion in August 2021. This acquisition expanded Danaher's presence in the genomic medicine field, complementing its existing diagnostics and life sciences businesses. |
Danaher Corporation and Aldevron |
|
In January 2023, bioMérieux acquired Specific Diagnostics, a company specializing in rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This acquisition enhanced bioMérieux's portfolio in combating antimicrobial resistance, a critical challenge in clinical microbiology. |
bioMérieux SA and Specific Diagnostics |
Market Regional Insights:
The global Clinical Microbiology Market exhibits varying growth patterns across different regions, influenced by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, prevalence of infectious diseases, and technological adoption. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, while Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing region. The market landscape is shaped by regional healthcare policies, research and development activities, and the presence of key industry players. Understanding these regional dynamics is crucial for stakeholders looking to capitalize on market opportunities and address region-specific challenges.
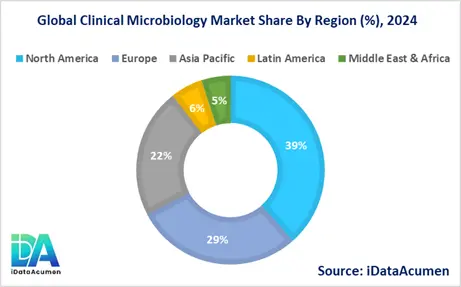
- North America is expected to be the largest market for Clinical Microbiology Market during the forecast period, accounting for over 38.5% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the advanced healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of innovative technologies, and significant investments in research and development. The presence of major market players and favorable reimbursement policies also contribute to the region's market dominance.
- The European market is expected to be the second-largest market for Clinical Microbiology Market, accounting for over 28.7% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market is attributed to the increasing focus on antimicrobial resistance, stringent regulatory standards for diagnostic testing, and growing awareness about the importance of early and accurate diagnosis of infectious diseases.
- The Asia-Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Clinical Microbiology Market, with a CAGR of over 7.2% during the forecast period by 2024. The growth of the market in Asia-Pacific is attributed to the rapidly improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising prevalence of infectious diseases in densely populated countries. This region also represents the third largest share, accounting for 22.3% of the global market.
Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Consumables
- Software & Services
- By Application
- Respiratory Diseases
- Bloodstream Infections
- Gastrointestinal Diseases
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Periodontal Diseases
- Others (e.g., wound infections, central nervous system infections)
- By Technology
- Culture-Based Methods
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Immunodiagnostics
- Microscopy
- Mass Spectrometry
- Others (e.g., biochemical tests, antibiotic susceptibility testing)
- By End User
- Hospitals & Diagnostic Centers
- Clinical Laboratories
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Others (e.g., blood banks, home healthcare settings)
- By Test Type
- Microbial Identification Tests
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Tests
- Blood Culture Tests
- Urine Culture Tests
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests
- Others (e.g., stool culture tests, mycology tests)
- By Disease Area
- Bacterial Infections
- Viral Infections
- Fungal Infections
- Parasitic Infections
- Others (e.g., prion diseases, mycobacterial infections)
- By Specimen Type
- Blood
- Urine
- Respiratory Samples
- Stool
- Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Genital Swabs
- Others (e.g., tissue samples, wound swabs)
- By Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Market Segmental Analysis:
Product Type Segment: The Reagents segment is projected to be the largest in 2024, accounting for approximately 40% of the market share. This segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2024 to 2031. The growth is particularly strong in the Asia-Pacific region, where it's anticipated to achieve a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period. The dominance of the Reagents segment is attributed to the recurring nature of reagent purchases and the increasing demand for ready-to-use, standardized diagnostic kits.
The Instruments segment is forecasted to be the second-largest in 2024, with about 30% market share. However, it's expected to show the fastest growth among all product types, with a CAGR of 6.8% globally. North America is likely to maintain its leadership in this segment due to rapid adoption of advanced automated systems.
Technology Segment: Molecular Diagnostics is anticipated to be the largest technology segment in 2024, capturing around 35% of the market share. This segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.1% globally, with the European market showing particularly strong growth at 7.8% CAGR. The increasing adoption of PCR and NGS technologies for pathogen detection is driving this segment's growth.
Culture-Based Methods, while traditional, are expected to remain the second-largest segment in 2024, with about 25% market share. However, this segment is likely to show slower growth compared to molecular methods, with a global CAGR of 4.5%.
End User Segment: Hospitals & Diagnostic Centers are projected to be the largest end-user segment in 2024, accounting for approximately 45% of the market share. This segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% globally, with significant growth in emerging markets of Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
Clinical Laboratories are anticipated to be the second-largest segment and the fastest-growing, with a global CAGR of 6.5%. The North American market is expected to lead in this segment, driven by the increasing trend of outsourcing diagnostic testing to specialized laboratories.
These projections highlight the dynamic nature of the Clinical Microbiology Market, with technological advancements and changing healthcare practices significantly influencing segment growth across different regions.
Top Companies in the Clinical Microbiology Market:
- BioMérieux SA
- Danaher Corporation (Cepheid)
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Roche Diagnostics
- Abbott Laboratories
- Bruker Corporation
- Siemens Healthineers
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Sysmex Corporation
- Hologic, Inc.
- Accelerate Diagnostics, Inc.
- Luminex Corporation (acquired by DiaSorin)
- OpGen, Inc.
- T2 Biosystems, Inc.
- Merck KGaA
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Meridian Bioscience, Inc.
- Quidel Corporation