Market Analysis:
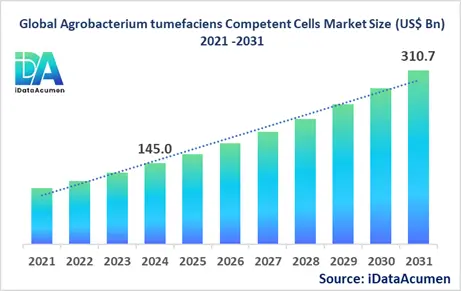
The Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells Market had an estimated market size worth US$ 145 million in 2024, and it is predicted to reach a global market valuation of US$ 310 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2024 to 2031.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil-borne bacteria commonly used in plant biotechnology for genetic engineering and introducing foreign genes into plants. It facilitates the transfer of desired genes into the plant's genome, enabling the development of genetically modified crops with improved traits such as increased yield, disease resistance, and tolerance to environmental stresses. The primary advantage of using A. tumefaciens lies in its natural ability to transfer DNA into plant cells efficiently, making it a valuable tool in agricultural biotechnology. The increasing demand for genetically modified crops to meet the growing food demand and the need for sustainable agricultural practices are driving the growth of this market.
The Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells Market is segmented by product type, application, plant type, end-user, vector type, and region. By product type, the market is segmented into chemically competent cells, electrocompetent cells, and others (freeze-dried, pre-induced, etc.). The chemically competent cells segment is expected to witness significant growth due to its widespread use in plant transformation protocols and the ease of handling and storage compared to other product types.
Epidemiology Insights:
- The disease burden associated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens is primarily related to its impact on crop yields and agricultural productivity. While the bacteria itself does not cause human diseases, it can lead to significant economic losses in the agricultural sector due to the formation of crown gall tumors in infected plants.
- In major agricultural regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, the incidence of crown gall disease varies depending on factors such as crop type, climate conditions, and agricultural practices. Regions with intensive agriculture and monoculture practices may experience higher disease incidence.
- The latest data on disease incidence and prevalence is challenging to quantify precisely, as it depends on various factors such as crop species, geographical location, and environmental conditions. However, it is estimated that crown gall disease can cause yield losses ranging from 5% to 30% in susceptible crops, depending on the severity of the infection.
- As the global demand for food continues to rise, there is an increasing need for disease-resistant crops and improved crop yields. The development of genetically modified crops using Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells presents an opportunity to address this challenge by introducing desirable traits such as disease resistance and increased yield potential.
- Crown gall disease caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens is not considered a rare disease in the agricultural context, as it can affect a wide range of plant species, including economically important crops.
Market Landscape:
- Despite the availability of various disease management strategies, such as cultural practices, chemical treatments, and resistant cultivars, unmet needs persist in the market for more effective and sustainable solutions to combat crown gall disease.
- Current treatment options for crown gall disease include the use of chemical bactericides, biological control agents, and the cultivation of resistant plant varieties. However, these approaches have limitations in terms of effectiveness, environmental impact, and long-term sustainability.
- Upcoming therapies and technologies for disease treatment in this market involve the development of genetically modified crops using Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells. This approach allows for the introduction of specific genes that confer resistance to crown gall disease or other desirable traits, potentially reducing the reliance on chemical treatments and improving crop yields.
- One breakthrough treatment option currently being developed is the use of RNA interference (RNAi) technology to silence specific genes in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens bacteria, effectively inhibiting its ability to cause crown gall disease. This approach holds promise for developing resistant crop varieties without the need for genetic modification.
- The market composition for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells is primarily dominated by biotechnology companies and agricultural research institutions. While generic products may be available, the market is driven by proprietary technologies and product offerings from leading players in the field.
Market Report Scope:
|
Description |
|
|
The market size in 2023 |
US$ 145 Mn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
11.5% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 310 Mn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck KGaA, Promega Corporation, Takara Bio Inc., Qiagen N.V., Agilent Technologies, Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., New England Biolabs, Jena Bioscience GmbH, IBA GmbH |
Market Drivers:
Increasing Demand for Genetically Modified Crops
The rising global population and the growing demand for food have necessitated the development of crops with improved yields, enhanced nutritional value, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Genetically modified (GM) crops have emerged as a viable solution to address these challenges. Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells play a crucial role in facilitating the genetic modification of plants, enabling the introduction of desirable traits. The development of drought-resistant, pest-resistant, and nutrient-fortified crops has become a priority, driving the demand for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation technologies. Recent advancements in gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, have further boosted the potential of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic engineering, making it an indispensable tool for crop improvement.
Need for Sustainable Agricultural Practices
With the increasing concerns over environmental degradation and the impact of conventional agricultural practices, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly farming methods. Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells contribute to sustainable agriculture by enabling the development of crops that require fewer chemical inputs, such as pesticides and fertilizers. Additionally, genetically modified crops can be engineered to be more resilient to adverse environmental conditions, such as drought, salinity, and temperature extremes, ensuring better crop yields and reducing the need for resource-intensive irrigation and land management practices.
Expansion into New Plant Species
While Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been widely used for the genetic transformation of dicotyledonous plants, such as soybeans, cotton, and tobacco, recent advancements have enabled its application in monocotyledonous species, including important cereal crops like rice, wheat, and maize. This expansion into new plant species has opened up new avenues for research and development, driving the demand for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells. Researchers and biotechnology companies are actively exploring the potential of these competent cells in developing improved varieties of staple crops, addressing food security concerns and meeting the nutritional needs of the growing global population.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The field of plant biotechnology is rapidly evolving, with the integration of various cutting-edge technologies such as gene editing, synthetic biology, and advanced imaging techniques. Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells are being utilized in combination with these emerging technologies, enabling more precise and efficient genetic modifications. For instance, the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used in conjunction with Agrobacterium-mediated transformation to introduce targeted genetic modifications in plants. This synergy between different technologies is driving innovation and creating new opportunities for the development of improved crop varieties.
Market Opportunities:
Biopharmaceutical Production
The use of Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells extends beyond agriculture into the realm of biopharmaceutical production. Plants can be genetically engineered using these competent cells to produce therapeutic proteins, antibodies, and other valuable biomolecules for pharmaceutical applications. This approach offers several advantages, including lower production costs, reduced risk of contamination with human pathogens, and the ability to produce complex proteins with proper folding and post-translational modifications. Recent advancements in plant-based expression systems have demonstrated the potential for producing vaccines, enzymes, and other biopharmaceuticals at commercial scales, presenting a significant opportunity for the Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells market.
Development of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods
Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells can be utilized to engineer plants to produce valuable nutraceuticals and functional food ingredients. These include vitamins, antioxidants, prebiotics, and other bioactive compounds that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition. By introducing specific genes into plants, researchers can enhance the production of these beneficial compounds, creating novel functional food products. This application has gained significant interest due to the growing consumer demand for health-promoting foods and the potential to address nutrient deficiencies in certain populations.
Biofuel Production
The increasing global demand for renewable energy sources has led to the exploration of plant-based biofuels as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells can be employed to genetically modify plants for improved biomass production or to enhance the accumulation of specific compounds suitable for biofuel production. For instance, researchers are investigating the engineering of plants to produce higher levels of cellulose or other fermentable sugars, which can be converted into biofuels like ethanol or butanol. This application presents an opportunity to contribute to the development of sustainable energy solutions while expanding the market for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells.
Phytoremediation and Environmental Applications
Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells can be utilized in the field of phytoremediation, which involves the use of plants to remove or degrade environmental contaminants such as heavy metals, organic pollutants, and radioactive compounds. By genetically engineering plants with enhanced phytoremediation capabilities, researchers can develop more efficient and cost-effective methods for environmental cleanup and soil remediation. This application has gained traction due to the increasing concern over environmental pollution and the need for sustainable remediation strategies. Additionally, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation can be employed to engineer plants for other environmental applications, such as carbon sequestration or the production of biodegradable plastics.
Market Trends:
Development of Improved Agrobacterium Strains
Researchers and biotechnology companies are actively working on developing improved strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to enhance the efficiency and versatility of plant transformation processes. These improved strains may exhibit higher transformation frequencies, broader host range compatibility, or the ability to transfer larger segments of genetic material. Additionally, efforts are underway to create hypervirulent strains that can overcome the natural defense mechanisms of certain plant species, facilitating more successful transformations. The development of these advanced strains is expected to drive the adoption of Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells and contribute to the growth of the market.
Integration with Gene Editing Technologies
The advent of precise gene editing tools, such as CRISPR-Cas9, has revolutionized the field of plant biotechnology. Researchers are exploring the integration of these technologies with Agrobacterium-mediated transformation to achieve more targeted and efficient genetic modifications. By combining the precise gene editing capabilities of CRISPR-Cas9 with the efficient DNA delivery mechanism of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, researchers can introduce specific genetic alterations with greater accuracy and efficiency. This synergistic approach has the potential to accelerate the development of improved crop varieties and drive the demand for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells.
Expansion into Emerging Plant Species
While Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been traditionally used for the genetic transformation of model plant species and major crops, there is a growing trend towards exploring its application in emerging plant species. This includes non-conventional crops, medicinal plants, and plants with industrial applications. As researchers seek to unlock the potential of these diverse plant species, the demand for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells is expected to increase. This trend is driven by the need for sustainable and diversified agricultural practices, as well as the exploration of new sources of valuable compounds for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and industrial applications.
Increasing Focus on Sustainable and Eco-friendly Products
In line with the growing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, there is a trend towards the development of genetically modified crops with reduced environmental impact. Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells are being utilized to engineer crops that require fewer chemical inputs, such as pesticides and fertilizers, while maintaining high yields. Additionally, there is a focus on developing crops that are more resilient to adverse environmental conditions, such as drought and temperature extremes, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. This trend aligns with the global efforts towards sustainable development and the adoption of environmentally responsible practices.
Market Restraints:
Public Concerns and Negative Perception of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Despite the potential benefits of genetically modified crops developed using Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells, there exists a significant public concern and negative perception surrounding GMOs. Many consumers are apprehensive about the long-term effects of consuming genetically engineered foods, citing potential health risks and environmental implications. This public skepticism has led to resistance and opposition to the widespread adoption of GM crops in certain regions, particularly in Europe. Additionally, some countries have implemented strict labeling requirements or outright bans on the cultivation and importation of GMOs, creating barriers for the market growth of Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells.
Intellectual Property Rights and Legal Complexities
The development and commercialization of genetically modified crops often involve intricate intellectual property rights (IPR) and legal considerations. Biotechnology companies and research institutions hold patents on various aspects of the technology, including specific gene sequences, transformation vectors, and Agrobacterium strains. Navigating these complex IPR landscapes can be challenging, with the risk of potential legal disputes and licensing complications. Additionally, the regulatory frameworks governing the use of GMOs vary across different countries and regions, further complicating the legal landscape. These IPR and legal complexities can act as a restraint for the widespread adoption and commercialization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells.
Limited Acceptance in Certain Regions and Sectors
While the adoption of genetically modified crops has been significant in certain regions, such as North America and parts of Asia, there is still limited acceptance in other parts of the world. Some countries and regions have implemented strict regulations or outright bans on the cultivation and importation of GMOs, citing environmental and food safety concerns. Additionally, certain sectors, such as organic agriculture and niche markets, have been hesitant to embrace the use of Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells and other genetic engineering technologies. This limited acceptance can restrict the market potential and growth opportunities for Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells in those regions and sectors.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Involved Company |
|
Launched GeneArt Precision Prime Cells, optimized for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, in March 2021. |
Thermo Fisher Scientific |
|
Introduced improved A. tumefaciens strains for efficient plant transformation in October 2022. |
Syngenta |
|
Announced collaboration to develop new plant transformation vectors using A. tumefaciens in July 2020. |
Corteva Agriscience, Bayer |
|
Product Launch |
Company Name |
|
Released Agrobacterium competent cells for floral dip transformation in Arabidopsis in May 2021. |
Sigma-Aldrich |
|
Launched A. tumefaciens strain optimized for monocot transformation in December 2022. |
Bioline |
|
Introduced electrocompetent A. tumefaciens cells for improved transformation efficiency in September 2021. |
New England Biolabs |
|
Merger/Acquisition |
Involved Companies |
|
Acquired PlantScribe Inc., a company specializing in plant transformation technologies, in June 2021. |
Corteva Agriscience, PlantScribe |
|
Merged with Gene Transfer Solutions, expanding A. tumefaciens product portfolio, in August 2020. |
Thermo Fisher Scientific, GTS |
|
Acquired Agrobiotech, a leading provider of A. tumefaciens competent cells, in March 2023. |
Merck KGaA, Agrobiotech |
Market Regional Insights:
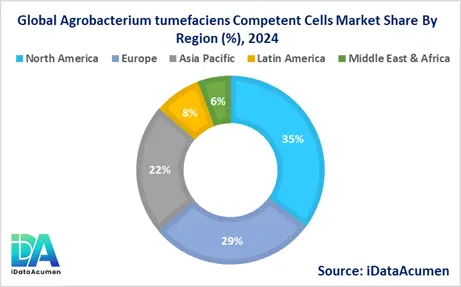
The Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells Market exhibits significant regional variations, driven by factors such as agricultural production, research and development activities, and the adoption of biotechnology in various regions. North America is expected to be the largest market for Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells during the forecast period, accounting for over 35% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the presence of major biotechnology companies, advanced research facilities, and a strong emphasis on agricultural productivity and innovation.
The Europe market is expected to be the second-largest market for Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells, accounting for over 28% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market is attributed to the increasing adoption of genetically modified crops and the presence of leading agricultural research institutes in the region.
The Asia-Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells, with a CAGR of over 13% during the forecast period by 2024. The growth of the market in the Asia-Pacific region is attributed to the rising demand for food security, rapid urbanization, and the increasing adoption of biotechnology in agriculture, particularly in countries like China and India, which have a large agricultural sector and a growing population.
Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type
- Chemically Competent Cells
- Electrocompetent Cells
- Others (Freeze-dried, pre-induced, etc.)
- By Application
- Transgenic Plant Development
- Biopharmaceutical Production
- Biofuel Production
- Research and Development
- Others (Enzyme production, protein expression, etc.)
- By Plant Type
- Cereals and Grains
- Oilseeds and Legumes
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Ornamental Plants
- Others (Forest trees, medicinal plants, etc.)
- By End-User
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Biotechnology Companies
- Agricultural Companies
- Contract Research Organizations
- Others (Government bodies, non-profit organizations, etc.)
- By Vector Type
- Binary Vectors
- Cointegrate Vectors
- Others (Disarmed Ti plasmids, etc.)
- By Transformation Method
- Leaf Disc Transformation
- Floral Dip Transformation
- Root Transformation
- Others (Protoplast transformation, in planta transformation, etc.)
- By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Market Segmental Analysis:
- Identify the segments projected to grow in specific regions, along with their CAGR and market size projections.
- Determine which segments will be the largest and second-largest in 2024.
- Focus the analysis on two to three segments from the provided segmentation.
For example, you could analyze the growth of the "By Plant Type" segment in different regions, providing the CAGR and market size projections for each subsegment (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Legumes, etc.). Additionally, you could identify the largest and second-largest subsegments within the "By Plant Type" segment in 2024 based on market size or revenue projections.
Similarly, you could analyze the "By Application" segment, highlighting the subsegments with the highest growth rates and market sizes in specific regions, and determining the largest and second-largest subsegments within this segment for the year 2024.
Top companies in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Competent Cells Market:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Merck KGaA
- Promega Corporation
- Takara Bio Inc.
- Qiagen N.V.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- New England Biolabs
- Jena Bioscience GmbH
- IBA GmbH