Market Analysis:
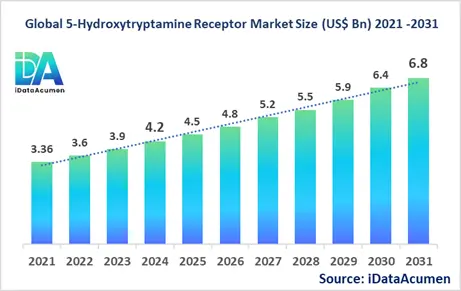
The 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Receptor Market had an estimated market size worth US$ 4.2 billion in 2024, and it is predicted to reach a global market valuation of US$ 6.8 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2024 to 2031.
5-HT receptors, also known as serotonin receptors, are a class of G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. These receptors are the target of various pharmaceutical drugs, including many antidepressants, antipsychotics, anorectics, antiemetics, gastroprokinetics, antimigraine agents, hallucinogens, and entactogens. The primary advantage of 5-HT receptor-targeted drugs is their ability to modulate serotonergic activity, which plays a crucial role in regulating mood, appetite, sleep, memory, and learning.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of mental health disorders, increasing geriatric population, and expanding indications for 5-HT drugs in areas such as gastrointestinal and neurological disorders.
The 5-HT Receptor Market encompasses a wide range of pharmaceutical products that interact with various serotonin receptor subtypes to treat diverse medical conditions. The market is segmented by drug class, application, receptor subtype, route of administration, distribution channel, end-user, molecule type, and region. By drug class, the market is segmented into Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), Serotonin Antagonist and Reuptake Inhibitors (SARIs), Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs), Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs), 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists, and others. SSRIs represent the largest subsegment due to their widespread use in treating depression and anxiety disorders, with fewer side effects compared to older antidepressants.
Recent innovations in the market include the development of novel 5-HT receptor subtype-specific drugs. For instance, the FDA's approval of Spravato (esketamine) nasal spray by Janssen Pharmaceuticals in 2019 marked a significant milestone in depression treatment, as it targets the glutamate system while indirectly influencing serotonin levels.
Epidemiology Insights:
The burden of diseases related to serotonin dysfunction varies across major regions, with high prevalence rates observed in North America and Europe. In the United States, approximately 7.8% of adults experience major depressive disorder in a given year, while anxiety disorders affect about 19.1% of the population annually. In Europe, depression affects around 6.9% of the population, with higher rates in certain countries like France (10.0%) and Ireland (12.1%).
Key epidemiological trends include the growing recognition and diagnosis of mental health disorders, particularly in developed markets such as the US, EU5 (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK), and Japan. Increased awareness, reduced stigma, and improved access to mental health services are driving factors behind these changes. Moreover, the aging population in these regions contributes to the rising prevalence of mood disorders and neurodegenerative diseases that may benefit from 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies.
In terms of disease incidence and prevalence, major depressive disorder (MDD) affects an estimated 17.3 million US adults (7.1% of the population) each year. In the EU5, the 12-month prevalence of MDD ranges from 3.6% to 9.1%. Japan reports lower rates, with a 12-month prevalence of major depressive episodes at around 2.2%. However, cultural factors and underreporting may influence these figures.
The incidence of migraines, another condition often treated with 5-HT receptor drugs, is approximately 12% of the population in Western countries. In the US alone, about 39 million people suffer from migraines.
Growth opportunities in the 5-HT Receptor Market are closely tied to these epidemiological patterns. The increasing patient population, particularly in mental health disorders, presents a significant market for pharmaceutical companies. Additionally, the growing geriatric population worldwide is likely to drive demand for treatments targeting age-related conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
While most conditions targeted by 5-HT receptor drugs are not considered rare diseases, there are exceptions. For instance, carcinoid syndrome, which can be treated with 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, is relatively rare, affecting only about 27 per million people each year in the US.
The evolving understanding of serotonin's role in various physiological processes continues to expand potential applications for 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies, opening new avenues for growth in previously underserved patient populations.
Market Landscape:
Despite significant advances in the 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Receptor Market, several unmet needs persist. One major challenge is the delayed onset of action for many antidepressants, which can take weeks to achieve therapeutic effects. This delay can be critical for patients with severe depression or suicidal ideation. Additionally, a substantial portion of patients (approximately 30-40%) do not respond adequately to first-line treatments, highlighting the need for more effective therapies.
Current treatment options in the market include a wide range of approved therapies. SSRIs such as fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and escitalopram (Lexapro) are commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety disorders. SNRIs like venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) offer an alternative for those who don't respond well to SSRIs. For migraine prevention, 5-HT1 receptor agonists (triptans) such as sumatriptan (Imitrex) are widely used. In the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists like ondansetron (Zofran) have become standard of care.
The market is witnessing the emergence of novel therapies and technologies. Esketamine (Spravato), a nasal spray targeting the NMDA receptor but indirectly affecting the serotonergic system, represents a breakthrough for treatment-resistant depression. Another exciting development is the exploration of psychedelics like psilocybin, which act on 5-HT2A receptors and show promise for depression and anxiety disorders.
Several breakthrough treatments are currently under development. These include:
- Vortioxetine (Trintellix), a multimodal antidepressant that acts as a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, and serotonin reuptake inhibitor, offering a unique mechanism of action.
- Novel 5-HT7 receptor antagonists are being investigated for their potential in treating depression and cognitive impairment.
- Selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists are in clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease, targeting cognitive deficits.
- Research into biased agonists, which selectively activate beneficial signaling pathways while minimizing side effects, could revolutionize drug development in this space.
The market composition for 5-HT receptor drugs is mixed. While there is a strong presence of generic manufacturers due to patent expirations of blockbuster drugs like Prozac and Paxil, branded drug manufacturers continue to play a significant role. Companies like Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline have historically dominated with branded products. However, the landscape is evolving with the entry of smaller biotech firms focusing on novel mechanisms and underserved indications within the 5-HT receptor space.
This dynamic market composition fosters both price competition from generics and continued innovation from branded manufacturers, driving the development of next-generation therapies to address existing unmet needs.
Market Report Scope:
|
Key Insights |
Description |
|
The market size in 2024 |
US$ 4.2 Bn |
|
CAGR (2024 - 2031) |
7.2% |
|
The revenue forecast in 2031 |
US$ 6.8 Bn |
|
Base year for estimation |
2024 |
|
Historical data |
2019-2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2031 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Million, and CAGR from 2021 to 2030 |
|
Market segments |
|
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Drivers |
|
|
Market Restraints |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
Pfizer Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline plc, AstraZeneca plc, Merck & Co. Inc., Johnson & Johnson, H. Lundbeck A/S, Novartis AG, Sanofi S.A., Roche Holding AG, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Alkermes plc, Allergan plc (now part of AbbVie), Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Mylan N.V. (now part of Viatris), Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bausch Health Companies Inc., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co. Ltd. |
Market Drivers:
Rising Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders
The escalating global burden of mental health disorders stands as a primary driver for the 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Receptor Market. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, which are intricately linked to serotonergic dysfunction, have seen a marked increase in prevalence. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that depression alone affects more than 264 million people worldwide, a figure that has grown significantly over the past decade.
This surge can be attributed to various factors, including heightened stress levels, socio-economic pressures, and the ongoing impact of global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic has exacerbated mental health issues, with studies indicating a substantial rise in symptoms of depression and anxiety among the general population. For instance, a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Network Open found that the prevalence of depressive symptoms was more than three-fold higher during the pandemic compared to before.
The increasing recognition of these disorders has led to greater diagnostic rates and a growing demand for effective treatments. Consequently, healthcare systems and policymakers are prioritizing mental health, allocating more resources to research, prevention, and treatment strategies that often involve 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies.
Moreover, high-profile awareness campaigns and the de-stigmatization of mental health issues have encouraged more individuals to seek help, further driving the need for innovative serotonergic drugs. This cultural shift, coupled with the stark realities of mental health statistics, underscores the critical role of the 5-HT Receptor Market in addressing one of the most pressing health challenges of our time.
Expanding Therapeutic Applications of 5-HT Receptor Drugs
The versatility of 5-HT receptors has opened doors to an array of therapeutic applications beyond traditional psychiatric indications, significantly propelling the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market. Researchers continue to uncover the pivotal roles these receptors play in various physiological processes, leading to novel drug development opportunities across multiple medical specialties.
In the realm of neurology, 5-HT1 receptor agonists (triptans) have revolutionized migraine treatment, offering relief to millions who suffer from this debilitating condition. The success of these agents has spurred further research into preventive therapies targeting different 5-HT receptor subtypes, aiming to reduce migraine frequency and severity.
Gastrointestinal disorders represent another frontier for 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies. The approval of drugs like alosetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), has demonstrated the potential of modulating serotonergic activity to alleviate GI symptoms. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of 5-HT4 receptor agonists in treating conditions such as chronic constipation and gastroparesis.
The role of serotonin in pain perception has also garnered attention, with SNRIs like duloxetine gaining indications for chronic pain conditions, including fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathy. This cross-over into pain management broadens the patient base for 5-HT receptor drugs and highlights their multifaceted therapeutic value.
Furthermore, emerging research points to potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Preclinical studies suggest that targeting specific 5-HT receptors may offer neuroprotective effects and cognitive benefits in conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. While still in early stages, these findings underscore the vast untapped potential of the 5-HT system in addressing unmet medical needs.
Advancements in Drug Delivery and Formulation Technologies
Innovation in drug delivery systems and formulation technologies is revolutionizing the administration of 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies, driving growth in the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market. These advancements aim to enhance drug efficacy, improve patient compliance, and minimize side effects—persistent challenges in the treatment of disorders involving serotonergic pathways.
One notable breakthrough is the development of long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotics and antidepressants. By providing sustained drug release over weeks or even months, LAIs address the critical issue of medication adherence in patients with severe mental illnesses. This is particularly significant given that non-adherence rates in psychiatric populations can exceed 50%, leading to relapse and rehospitalization.
Transdermal delivery systems represent another innovative approach, offering a non-invasive alternative that bypasses first-pass metabolism and allows for steady drug absorption. Patches delivering serotonergic agents have shown promise in maintaining consistent plasma levels while reducing gastrointestinal side effects commonly associated with oral medications.
The intranasal route has gained traction following the approval of esketamine nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression. This method facilitates rapid drug absorption and onset of action, crucial for patients in acute distress. The success of esketamine has paved the way for exploring intranasal delivery of other serotonergic compounds, potentially transforming emergency and outpatient psychiatric care.
Additionally, advances in nanoformulation are enabling enhanced brain targeting of 5-HT receptor drugs. Nanocarriers can improve the blood-brain barrier permeability of these agents, increasing central bioavailability while minimizing systemic exposure. This not only boosts therapeutic efficacy but also reduces off-target effects, a key consideration in improving tolerability and patient acceptance of psychotropic medications.
Growing Geriatric Population and Age-Related Disorders
The global demographic shift towards an aging population is a significant driver for the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market. According to the United Nations, the number of persons aged 65 or above is projected to double to 1.5 billion by 2050. This trend has profound implications for healthcare, particularly in the realm of mental health and neurological disorders where serotonergic dysfunction often plays a central role.
Older adults are disproportionately affected by conditions such as late-life depression, anxiety disorders, and cognitive impairment. The complex interplay between age-related changes in brain chemistry, chronic medical conditions, and psychosocial factors contributes to the high prevalence of these disorders in the elderly. For instance, studies indicate that up to 13.5% of older individuals meet the criteria for a depressive disorder, highlighting a substantial need for effective serotonergic therapies tailored to this population.
Moreover, the aging process itself is associated with alterations in the serotonin system. Research has shown age-dependent decreases in 5-HT receptor density and serotonin transporter availability, which may predispose older adults to mood and cognitive disturbances. These neurobiological changes underscore the relevance of 5-HT receptor-targeted interventions in promoting healthy aging and maintaining quality of life in later years.
The geriatric cohort also faces unique challenges in pharmacotherapy, such as altered drug metabolism, increased sensitivity to side effects, and potential drug-drug interactions due to polypharmacy. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on developing 5-HT receptor drugs with improved safety profiles and formulations suitable for older patients. Extended-release preparations, lower-dose options, and medications with reduced anticholinergic burden are examples of innovations addressing these needs.
Furthermore, the rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's in the aging population is spurring research into the neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties of serotonergic agents. Preliminary evidence suggests that modulating specific 5-HT receptor subtypes may offer benefits in memory, executive function, and even disease-modifying effects, opening new avenues for drug development in this critical area.
Market Opportunities:
Personalized Medicine in Psychiatric Care
The advent of personalized medicine presents a transformative opportunity for the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market. Despite the availability of numerous serotonergic drugs, response rates in psychiatric disorders remain suboptimal, with a significant proportion of patients failing to achieve remission on first-line treatments. This challenge stems from the heterogeneity of conditions like depression and the inter-individual variability in drug metabolism and receptor sensitivity.
Pharmacogenomics is at the forefront of tailoring 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies to individual patients. Genetic variations in serotonin transporters (SLC6A4), metabolic enzymes (CYP2D6, CYP2C19), and receptor genes (HTR1A, HTR2A) have been linked to differential treatment outcomes. By identifying these biomarkers, clinicians can potentially predict a patient's likelihood of response or risk of adverse effects to specific serotonergic agents.
Recent strides in this field include the development of combinatorial pharmacogenomic tests, which analyze multiple genes involved in antidepressant response. A landmark study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research demonstrated that patients whose treatment was guided by such a test experienced significantly higher rates of remission compared to those receiving treatment as usual.
The integration of neuroimaging techniques, such as PET scans visualizing 5-HT receptor occupancy, further enhances the precision of drug selection and dosing. These tools can provide insights into an individual's baseline serotonergic function and help monitor treatment-induced changes, allowing for dynamic therapy adjustments.
Moreover, the burgeoning field of digital phenotyping leverages smartphone data and wearable devices to capture real-time behavioral and physiological markers relevant to mood disorders. When combined with genetic information, these digital biomarkers could revolutionize the way we diagnose, monitor, and treat conditions linked to serotonergic dysregulation.
As healthcare systems increasingly recognize the economic and clinical benefits of personalized approaches, the 5-HT Receptor Market stands poised to deliver targeted solutions that optimize patient outcomes and resource utilization. The realization of this opportunity not only promises to improve the lives of those with psychiatric illnesses but also to reshape the landscape of mental health care delivery.
Innovative Combination Therapies
The exploration of innovative combination therapies represents a fertile ground for growth in the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market. As the complexity of disorders involving serotonergic pathways becomes increasingly apparent, there is a growing recognition that monotherapy may not suffice for all patients. Combining agents that target different aspects of the 5-HT system or complementary neurotransmitter systems offers the potential to enhance efficacy, mitigate side effects, and address treatment-resistant cases.
One promising avenue is the pairing of traditional serotonergic drugs with agents that modulate other monoamines or neuropeptides. For instance, the combination of SSRIs with atypical antipsychotics has shown superior results in major depressive disorder with inadequate response to antidepressants alone. The synergistic effects on serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine receptors can yield broader symptom improvement and faster onset of action.
Similarly, augmenting 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies with drugs that influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis or neurotropic factors may tackle the multifaceted nature of stress-related disorders. Clinical trials investigating the co-administration of SSRIs and CRH receptor antagonists or BDNF-enhancing compounds exemplify this trend towards holistic treatment strategies.
In the realm of pain management, combining serotonergic agents with novel analgesics is garnering interest. The dual-mechanism approach of SNRIs and gabapentinoids has already proven beneficial in neuropathic pain conditions. Future developments may include pairings with cannabinoids, NMDA receptor modulators, or targeted cytokine inhibitors to provide comprehensive pain relief while minimizing opioid use.
The concept of rational polypharmacy extends to other therapeutic areas where 5-HT receptors play a role. In irritable bowel syndrome, for example, researchers are exploring combinations of 5-HT3 antagonists with drugs targeting motility or visceral hypersensitivity to achieve better symptom control.
Furthermore, advances in drug delivery technologies are facilitating the development of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) that improve patient adherence and pharmacokinetic profiles. Novel formulations that co-encapsulate serotonergic drugs with agents having complementary mechanisms could streamline treatment regimens and reduce pill burden.
As regulatory agencies become more receptive to well-designed combination products addressing clear unmet needs, the 5-HT Receptor Market has an opportunity to pioneer integrated therapeutic solutions. By leveraging the diverse functions of serotonin and its interplay with other physiological systems, these innovative approaches have the potential to transform outcomes across a spectrum of challenging disorders.
Targeting Neglected 5-HT Receptor Subtypes
The 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market stands on the cusp of a new frontier: harnessing the therapeutic potential of previously neglected 5-HT receptor subtypes. While SSRIs and other drugs targeting major serotonin receptor classes have dominated the landscape, growing evidence suggests that less-explored subtypes may hold the key to treating refractory conditions and expanding the reach of serotonergic therapies.
5-HT6 receptors, predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, have emerged as a compelling target for cognitive enhancement. Preclinical studies have shown that 5-HT6 antagonists can improve memory and executive function, sparking interest in their application for Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, and attention deficit disorders. Early-phase clinical trials of compounds like idalopirdine and intepirdine, while not meeting primary endpoints, have provided valuable insights into dose optimization and patient selection for future development efforts.
Another intriguing candidate is the 5-HT7 receptor, implicated in circadian rhythm regulation, mood modulation, and thermoregulation. Selective 5-HT7 antagonists have demonstrated antidepressant and pro-cognitive effects in animal models, with the potential to address both affective and cognitive symptoms in complex disorders like bipolar depression. The recent discovery of biased ligands that can selectively activate beneficial signaling pathways of 5-HT7 receptors while minimizing desensitization opens new possibilities for fine-tuned therapeutic interventions.
In the periphery, 5-HT4 receptors are gaining attention for their role in gastrointestinal and cardiac function. Agonists of this subtype, such as prucalopride, have shown efficacy in chronic constipation by enhancing colonic motility. Ongoing research is investigating whether 5-HT4 modulation could also benefit conditions like gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, and even certain types of arrhythmias, given the receptor's presence in cardiac tissue.
The 5-HT5A receptor, one of the least characterized subtypes, is now under scrutiny for its involvement in cognitive processing and mood regulation. Although no selective ligands have reached clinical trials, preclinical findings hint at the receptor's relevance in conditions ranging from schizophrenia to substance abuse disorders.
Advances in structural biology and computational modeling are accelerating the design of subtype-specific ligands with improved selectivity and pharmacokinetic properties. High-resolution crystal structures of several 5-HT receptors have been elucidated, providing templates for rational drug discovery approaches targeting these neglected subtypes.
By focusing on these underexplored facets of the serotonin system, the 5-HT Receptor Market has an opportunity to develop truly novel therapeutics that address lingering unmet needs. Whether it's enhancing cognition in neurodegenerative diseases, tackling treatment-resistant depression, or revolutionizing the management of functional gastrointestinal disorders, drugs targeting neglected 5-HT subtypes could carve out entirely new market segments and therapeutic paradigms.
5-HT Receptors in Immunomodulation and Oncology
An emerging and potentially groundbreaking opportunity for the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market lies in the intersection of serotonergic signaling with immunology and oncology. Recent discoveries have illuminated the extensive presence of 5-HT receptors on immune cells and within the tumor microenvironment, suggesting roles far beyond neurotransmission. This newfound understanding is paving the way for innovative applications of 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies in modulating immune responses and combating cancer.
In the immune system, serotonin acts as a signaling molecule influencing lymphocyte activation, cytokine production, and cell migration. Different 5-HT receptor subtypes mediate diverse, sometimes opposing effects on immune function. For instance, 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptors have been implicated in pro-inflammatory responses, while 5-HT4 and 5-HT7 receptors appear to have anti-inflammatory properties. This nuanced control offers the potential to fine-tune immune reactions in autoimmune diseases, allergic conditions, and chronic inflammatory disorders.
Preclinical studies have already demonstrated promising results. In models of rheumatoid arthritis, selective 5-HT2A antagonists reduced joint inflammation and bone erosion. Similarly, 5-HT4 agonists showed protective effects in experimental colitis, highlighting possible applications in inflammatory bowel diseases. The repurposing of existing serotonergic drugs with well-established safety profiles could accelerate the translation of these findings into clinical immunomodulatory strategies.
The role of 5-HT receptors in oncology is a rapidly unfolding narrative. Accumulating evidence indicates that serotonin can act as a growth factor for certain cancers, promoting proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Conversely, some serotonergic pathways may have tumor-suppressive effects.
Market Trends:
- Increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies has led to a growing interest in 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors as potential drug targets. Researchers are exploring the diverse roles of 5-HT receptor subtypes in various physiological processes and pathological conditions, aiming to develop more selective and effective treatments. This trend is particularly evident in the field of neurology, where 5-HT receptors are implicated in disorders such as depression, anxiety, and migraine.
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of 5-HT receptor modulators in addressing treatment-resistant depression. For instance, the FDA approval of esketamine, which acts on the 5-HT system, has opened new avenues for patients who have not responded to conventional antidepressants. In the realm of migraine therapy, the emergence of 5-HT1F receptor agonists, such as lasmiditan, represents a breakthrough in providing relief without the cardiovascular side effects associated with older triptans.
The trend towards personalized medicine is further exemplified by ongoing research into genetic variations that influence individual responses to 5-HT receptor-targeting drugs. By identifying biomarkers and genetic polymorphisms, clinicians can tailor treatment plans to maximize efficacy and minimize adverse effects. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to the overall growth of the 5-HT receptor market.
Moreover, the expanding application of 5-HT receptor ligands in gastrointestinal disorders has garnered significant attention. Drugs targeting 5-HT4 receptors have shown promise in treating chronic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, addressing a large unmet medical need. The success of prucalopride and other emerging therapies in this space underscores the versatility of 5-HT receptors as therapeutic targets beyond the central nervous system.
- The convergence of neuroscience and immunology has shed light on the critical role of 5-HT receptors in neuroimmune interactions, driving research into novel therapeutic approaches for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. This trend is reshaping the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor market by expanding its scope beyond traditional psychiatric and neurological applications.
Recent discoveries have highlighted the presence of 5-HT receptors on immune cells and their involvement in modulating immune responses. For example, studies have shown that targeting 5-HT7 receptors can attenuate neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis models, offering a potential neuroprotective strategy. Similarly, the anti-inflammatory properties of 5-HT2B receptor antagonists are being investigated for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
The potential of 5-HT receptor modulators in treating systemic inflammatory conditions is further exemplified by ongoing clinical trials exploring their efficacy in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. These studies not only demonstrate the far-reaching impact of 5-HT signaling but also underscore the market's responsiveness to emerging scientific insights.
Additionally, the interplay between 5-HT receptors and the gut-brain axis has gained traction, with implications for both gastrointestinal and mental health disorders. Probiotics that influence 5-HT production and receptor function are being developed as adjunctive therapies, reflecting a holistic approach to treatment that resonates with consumer preferences for natural and integrative solutions.
- Advancements in drug delivery systems and formulation technologies are enhancing the therapeutic potential of 5-HT receptor-targeting agents, driving innovation in the market. These developments are addressing challenges such as poor bioavailability, suboptimal brain penetration, and side effects, thereby improving the clinical utility of existing and novel compounds.
One notable example is the use of nanoparticle-based delivery for 5-HT3 receptor antagonists in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. By encapsulating drugs like ondansetron in nanocarriers, researchers have achieved sustained release profiles and reduced systemic exposure, minimizing adverse reactions while maintaining efficacy. This approach not only benefits patients but also extends the commercial lifespan of established medications.
Similarly, the development of transdermal patches for 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists used in migraine treatment has gained momentum. Products like sumatriptan iontophoretic transdermal systems offer needle-free administration, rapid onset of action, and improved patient compliance. Such innovations cater to the growing demand for user-friendly and non-invasive drug delivery options.
Furthermore, the trend towards extended-release formulations is evident in the management of psychiatric disorders. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics that modulate 5-HT2A receptors, such as paliperidone palmitate, have transformed treatment paradigms for schizophrenia by ensuring consistent drug levels and reducing relapse rates. These formulations not only improve clinical outcomes but also address the significant challenge of medication adherence.
- The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in drug discovery and development is accelerating the identification of novel 5-HT receptor ligands and optimizing lead compounds. This trend is shortening research timelines, reducing costs, and increasing the success rates of clinical candidates, thereby invigorating the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor market.
Recent collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and AI firms have yielded promising results in designing selective 5-HT receptor modulators. For instance, in silico screening methodologies have facilitated the discovery of potent 5-HT6 receptor antagonists with potential applications in cognitive disorders and Alzheimer's disease. By leveraging vast chemical libraries and predictive algorithms, researchers can rapidly explore structure-activity relationships and prioritize molecules for synthesis and testing.
Moreover, AI-driven approaches are being employed to repurpose existing drugs that interact with 5-HT receptors for new indications. This strategy not only capitalizes on well-characterized safety profiles but also expedites the path to market. A case in point is the investigation of the antidepressant fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, for its anti-inflammatory properties mediated through 5-HT2B receptor antagonism.
The application of machine learning in pharmacogenomics is another facet of this trend, enabling the development of precision therapies targeting specific 5-HT receptor polymorphisms. By analyzing large datasets of genetic information and drug response data, researchers can identify patient subgroups most likely to benefit from particular interventions, paving the way for tailored treatment regimens.
Market Restraints:
- The complexity and heterogeneity of the serotonergic system pose significant challenges in developing highly selective 5-HT receptor ligands, which can impede progress in the market. With at least 14 distinct receptor subtypes identified, each with unique distribution patterns and signaling pathways, achieving targeted modulation without off-target effects remains a formidable task.
This complexity is exemplified by the historical difficulties in creating selective 5-HT2C receptor agonists for obesity treatment. Early candidates often exhibited activity at other 5-HT2 subtypes, leading to unintended cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric side effects. While recent advances, such as the approval of lorcaserin, have overcome some of these hurdles, its subsequent withdrawal due to cancer risk underscores the ongoing challenges in this space.
Similarly, the development of anxiolytics targeting 5-HT1A receptors has been hampered by the receptor's widespread distribution and involvement in diverse physiological processes. Compounds acting as full agonists can produce sedation and cognitive impairment, limiting their therapeutic utility. The pursuit of partial agonists or biased ligands that selectively engage beneficial signaling pathways is ongoing but fraught with obstacles.
Furthermore, the intricate interplay between different 5-HT receptor subtypes can lead to compensatory mechanisms that attenuate the desired effects of targeted interventions. For instance, chronic blockade of one receptor subtype may result in upregulation or sensitization of others, potentially negating therapeutic benefits or introducing new adverse reactions. This dynamic landscape necessitates a deep understanding of receptor crosstalk and adaptive responses, which can prolong drug development timelines and increase attrition rates.
- Regulatory hurdles and stringent safety requirements for central nervous system (CNS) drugs, which constitute a significant portion of 5-HT receptor-targeting therapeutics, can decelerate market growth. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) presents a formidable obstacle, necessitating extensive preclinical evaluations to ensure adequate brain penetration and minimize peripheral side effects.
Recent setbacks in late-stage clinical trials highlight the challenges faced by companies developing 5-HT receptor modulators for neurological and psychiatric indications. For example, the failure of several 5-HT6 receptor antagonists in Phase III studies for Alzheimer's disease, despite promising early results, has dampened enthusiasm and led to the reallocation of resources. Such high-profile disappointments not only represent substantial financial losses but also heighten investor wariness, potentially limiting funding for future endeavors.
Moreover, the long-term safety profiles required for chronic conditions often treated with 5-HT receptor-targeting drugs impose additional burdens on developers. Post-marketing surveillance has revealed rare but serious adverse events associated with certain agents, such as the risk of serotonin syndrome with SSRIs or cardiac valvulopathy with 5-HT2B receptor agonists used in the past for appetite suppression. These findings have prompted regulatory agencies to mandate comprehensive risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS), which can restrict prescribing and impact commercial viability.
The evolving regulatory landscape also demands rigorous assessment of abuse potential for drugs that modulate 5-HT receptors involved in reward pathways. The scheduling of new chemical entities under controlled substance acts can limit accessibility and prescriber willingness, as evidenced by the initial classification of esketamine as a Schedule III drug. Navigating these regulatory complexities requires substantial investment in abuse liability studies and the development of tamper-resistant formulations, factors that can deter smaller players from entering the market.
- Patent expirations and the subsequent influx of generic competition pose significant challenges to revenue sustainability in the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor market. As key drugs lose exclusivity, innovator companies face sharp declines in sales, which can disincentivize further research and development in established therapeutic areas.
The impact of genericization is particularly pronounced in the antidepressant segment, where many selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) have gone off-patent. For instance, the availability of generic escitalopram has not only eroded the market share of branded Lexapro but also intensified price pressures across the class. This phenomenon compels companies to either diversify their pipelines or pursue incremental innovations, such as extended-release formulations or combination products, which may offer limited differentiation.
Similarly, the migraine therapy landscape has been transformed by the generic availability of triptans, 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists that once dominated the market. While this improves patient access to affordable treatments, it also diminishes the commercial attractiveness of developing next-generation triptans. Consequently, research efforts have shifted towards novel mechanisms, such as CGRP antagonists, which, although promising, may not fully leverage the therapeutic potential of the serotonergic system.
The challenge of patent cliffs is further compounded by the difficulty in recouping R&D investments for 5-HT receptor-targeting drugs with niche indications. Orphan drug designations and exclusivity periods provide some protection, but the limited patient populations often translate to constrained revenue potential. This dynamic can discourage pharmaceutical companies from pursuing innovative therapies for rare diseases mediated by 5-HT receptors, despite the significant unmet medical needs.
Recent Developments:
|
Development |
Involved Company |
|
In March 2023, the FDA approved Zurzuvae (zuranolone), a first-in-class, rapid-acting oral treatment for postpartum depression. This approval marks a significant advancement in addressing an often underserved aspect of maternal mental health. |
Sage Therapeutics and Biogen |
|
Axsome Therapeutics received FDA approval for Auvelity (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in August 2022, the first oral N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist for major depressive disorder. This novel mechanism offers new hope for treatment-resistant patients. |
Axsome Therapeutics |
|
In September 2022, COMPASS Pathways announced positive topline results from its phase IIb clinical trial of COMP360 psilocybin therapy for treatment-resistant depression, potentially opening a new frontier in serotonergic therapies. |
COMPASS Pathways |
|
Lundbeck launched Vyepti (eptinezumab-jjmr) in April 2020, the first FDA-approved intravenous preventive treatment for migraine. This calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibitor offers a new option for patients with frequent migraines. |
Lundbeck |
|
In January 2021, Alkermes received FDA approval for Lybalvi (olanzapine and samidorphan), a novel antipsychotic that combines olanzapine with a mu-opioid receptor antagonist to mitigate weight gain, a common side effect. |
Alkermes |
|
Minerva Neurosciences announced positive results from its Phase 3 trial of roluperidone for negative symptoms in schizophrenia in December 2022, addressing a significant unmet need in schizophrenia treatment. |
Minerva Neurosciences |
|
In a major consolidation move, AbbVie completed its acquisition of Allergan in May 2020 for $63 billion, significantly expanding its presence in the neuroscience and mental health markets. |
AbbVie and Allergan |
|
Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and Roivant Sciences formed Sumitovant Biopharma in December 2019, a jointventure to accelerate development of innovative therapies, including those targeting neuropsychiatric disorders. |
Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and Roivant Sciences |
|
In September 2021, Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Lundbeck announced a global collaboration to develop and commercialize brexpiprazole in China, further expanding access to this important antipsychotic medication. |
Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Lundbeck |
Market Regional Insights:
The global 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Receptor Market exhibits significant regional variations in market size, growth drivers, and adoption rates of serotonergic therapies. These differences are influenced by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, prevalence of mental health disorders, reimbursement policies, and awareness levels. Understanding these regional dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to tailor their strategies and capitalize on growth opportunities across different geographies.
- North America is expected to be the largest market for 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market during the forecast period, accounting for over 42.5% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to the high prevalence of depression and anxiety disorders, robust healthcare infrastructure, and favorable reimbursement policies for mental health treatments. The U.S., in particular, leads in the adoption of novel therapies and has a strong pipeline of 5-HT receptor-targeted drugs.
- The Europe market is expected to be the second-largest market for 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market, accounting for over 28.7% of the market share in 2024. The growth of the market is attributed to the increasing recognition of mental health as a public health priority, government initiatives to improve access to psychiatric care, and the presence of major pharmaceutical companies engaged in neuroscience research.
- The Asia Pacific market is expected to be the fastest-growing market for 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market, with a CAGR of over 8.5% during the forecast period by 2024. The growth of the market in Asia Pacific is attributed to the rising awareness about mental health, improving healthcare access, and the large patient pool in countries like China and India. Additionally, increasing healthcare expenditure and the entry of global pharmaceutical players into the region are fueling market expansion. Asia Pacific currently holds the third-largest share at 18.3% of the global market.
Market Segmentation:
- By Drug Class
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Serotonin Antagonist and Reuptake Inhibitors (SARIs)
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
- 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists
- Others (5-HT1 Receptor Agonists, 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists)
- By Application
- Depression
- Anxiety Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder
- Migraine
- Schizophrenia
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Others (Eating Disorders, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder)
- By Receptor Subtype
- 5-HT1
- 5-HT2
- 5-HT3
- 5-HT4
- 5-HT5
- 5-HT6
- 5-HT7
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Injectable
- Transdermal
- Intranasal
- Others (Sublingual, Rectal)
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others (Mail-order Pharmacies, Clinics)
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Homecare Settings
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Others (Long-term Care Facilities, Rehabilitation Centers)
- By Molecule Type
- Small Molecules
- Biologics
- Biosimilars
- By Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Market Segmental Analysis:
In the 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Receptor Market, certain segments are poised for significant growth, driven by regional factors, technological advancements, and evolving treatment paradigms.
The Drug Class segment, particularly Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), is expected to maintain its dominance, especially in North America and Europe. With a projected CAGR of 6.8% through 2031, SSRIs will likely account for the largest market share due to their established efficacy and relatively favorable side effect profile in treating depression and anxiety disorders. However, Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) are anticipated to exhibit the fastest growth, with a CAGR of around 7.5%, driven by their increasing use in pain management and treatment-resistant depression.
Within the Application segment, Depression is forecast to remain the largest subsegment, reflecting the high global prevalence of depressive disorders. This subsegment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% and command over 40% of the market share by 2024. However, the Migraine subsegment is emerging as a high-growth area, particularly in the Asia Pacific region, where awareness and diagnosis rates are improving. With innovative 5-HT1 receptor agonists (triptans) and preventive therapies entering the market, this subsegment could see a CAGR exceeding 8% through 2031.
The Route of Administration segment presents interesting dynamics. While Oral administration currently dominates due to patient preference and the availability of numerous oral formulations, the Intranasal subsegment is projected to be the fastest-growing, with a CAGR of over 9%. This growth is largely attributed to the success of drugs like esketamine nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression, which offer rapid onset of action. North America is expected to lead in the adoption of intranasal therapies, but Europe and Asia Pacific are quickly following suit.
Regionally, while North America will continue to hold the largest market share across most segments, Asia Pacific is poised to witness the highest growth rates. This is particularly evident in the End User segment, where Hospitals and Specialty Clinics in countries like China, India, and South Korea are rapidly expanding their mental health services, driving demand for 5-HT receptor-targeted therapies.
Top companies in the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor Market:
- Pfizer Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- AstraZeneca plc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson
- H. Lundbeck A/S
- Novartis AG
- Sanofi S.A.
- Roche Holding AG
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Alkermes plc
- Allergan plc (now part of AbbVie)
- Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Mylan N.V. (now part of Viatris)
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Bausch Health Companies Inc.
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.